Bone Neoformation Induced by Low-Level Laser and Methylene Blue Suggests Early Ossification in Rats
- PMID: 37041788
- PMCID: PMC10082916
- DOI: 10.34172/jlms.2022.48
Bone Neoformation Induced by Low-Level Laser and Methylene Blue Suggests Early Ossification in Rats
Abstract
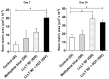
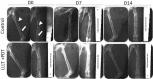
Introduction: Bone healing depends on inflammation control and tissue repair time. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) has been investigated to accelerate this process. Methylene blue (MB), together with LLLT, has been investigated for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential; however, the effects of photosensitizers (photodynamic therapy, PDT) are controversial. This study aimed to verify whether the combination of MB and LLLT changes the course of the consolidation of experimental bone defects. Methods: Sixteen Wistar rats underwent femoral bone defects. In the control group (n=4), LLLT simulations were performed without MB. The MB group (n=4) received MB and simulation of LLLT. The LLLT group (n=4) was exposed to LLLT. The PDT+LLLT group (n=4) received MB and LLLT. At the end of 7 or 14 days, the animals were euthanized, and samples were collected. Results: PDT and LLLT induced osteogenic formation with cellularity (after seven days) and union of bony edges (14 days). On the seventh day, LLLT combined with PDT induced an increase (P<0.05) of 484% in the area of bone neoformation compared to the control. On the fourteenth day, LLLT combined with PDT or alone increased (P<0.05) the area of bone neoformation by 214% and 240% respectively, compared to the control group. The PDT/LLLT combination was associated with increased radiopacity (P<0.038). Conclusion: The combined use of MB with LLLT initiated during the transoperative phase may stimulate the bone repair process in rats.
Keywords: Bone; Laser; Methylene blue; Ossification.
Copyright © 2022 J Lasers Med Sci.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histologic Evaluation of Early Bone Regeneration Treated with Simvastatin Associated with Low-Level Laser Therapy.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019 May/June;34(3):658–664. doi: 10.11607/jomi.6990. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019. PMID: 30892287
-
In vivo effect of photodynamic therapy on periodontal bone loss in dental furcations.J Periodontol. 2008 Jun;79(6):1081-8. doi: 10.1902/jop.2008.070456. J Periodontol. 2008. PMID: 18533787
-
Methylene Blue-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy Induces Macrophage Apoptosis via ROS and Reduces Bone Resorption in Periodontitis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Aug 14;2019:1529520. doi: 10.1155/2019/1529520. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31485288 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment with combined low-level laser therapy and methylene blue improves learning and memory in sleep-deprived mice.Lasers Med Sci. 2022 Jul;37(5):2403-2412. doi: 10.1007/s10103-021-03497-6. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Lasers Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35059872
-
High-intensity laser and photodynamic therapy as a treatment for recurrent herpes labialis.Photomed Laser Surg. 2010 Jun;28(3):439-44. doi: 10.1089/pho.2009.2522. Photomed Laser Surg. 2010. PMID: 19821702
Cited by
-
Low-Level Laser Therapy Effects on Reducing Surgical Complications and Wound Infection after Cesarean Section.Maedica (Bucur). 2023 Sep;18(3):426-431. doi: 10.26574/maedica.2023.18.3.426. Maedica (Bucur). 2023. PMID: 38023759 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction using methylene blue or mitoquinone to improve skeletal aging.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Mar 25;16(6):4948-4964. doi: 10.18632/aging.205147. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38535998 Free PMC article.
-
Photobiomodulation Therapy Improves Repair of Bone Defects Filled by Inorganic Bone Matrix and Fibrin Heterologous Biopolymer.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jan 13;11(1):78. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11010078. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Souza EQM, Costa Klaus AE, Espósito Santos BF, Carvalho da Costa M, Ervolino E, Coelho de Lima D, et al. Evaluations of hydroxyapatite and bioactive glass in the repair of critical size bone defects in rat calvaria. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2020;10(4):422–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2020.07.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous