Prenatal Morphine Exposure Increases Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Programs Neurogenic Hypertension in the Adult Offspring
- PMID: 37042247
- PMCID: PMC10274123
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.20262
Prenatal Morphine Exposure Increases Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Programs Neurogenic Hypertension in the Adult Offspring
Abstract
Background: The opioid overdose and opioid use disorder epidemics are concomitant with increased metabolic and CVD risk. Although opioid use disorder causes adverse pregnancy outcomes, the offspring's cardiovascular health is understudied. We hypothesized that offspring exposed to in utero morphine exposure (IUME) would show increased CVD risk factors and endogenous opioid system dysregulation.
Methods: Sprague Dawley dams were treated with saline (vehicle, n=10) or escalating doses of morphine (5-20 mg/kg per day, SC, n=10) during gestation. Cardiovascular and metabolic parameters were assessed in adult offspring.
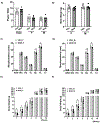
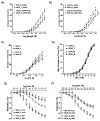
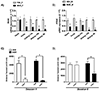
Results: Litter size and pups' birth weight were not different in response to IUME. Female and male IUME offspring showed reduced body length at birth (P<0.05) and body weight from weeks 1 to 3 of life (P<0.05), followed by a catch-up growth effect. By week 16, female and male IUME rats showed reduced tibia length (P<0.05) and fat mass. IUME increases the mean arterial pressure and the depressor response to mecamylamine (5 mg/kg per day, IP) induced by IUME were abolished by a chronic treatment with an alpha-adrenergic receptor blocker (prazosin; 1 mg/kg per day, IP). Although circulating levels of angiotensin peptides were similar between groups, IUME exacerbated maximal ex vivo Ang (angiotensin) II-induced vasoconstriction (P<0.05) and induced endothelial dysfunction in a sex-specific manner (P<0.05). Proenkephalin, an endogenous opioid peptide that lowers blood pressure and sympathetic-mediated vasoconstriction, showed reduced mRNA expression in the heart, aorta, and kidneys from morphine versus vehicle group (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Among the effects of IUME, neurogenic hypertension, vascular dysfunction, and metabolic dysfunction could be associated with the dysregulation of the endogenous opioid system.
Keywords: body weight; heroin; morphine; opioid peptide; prazosin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

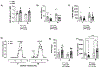

Similar articles
-
The effects of buprenorphine and morphine during pregnancy: Impact of exposure length on maternal brain, behavior, and offspring neurodevelopment.Neuropharmacology. 2024 Oct 1;257:110060. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.110060. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Neuropharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38960134
-
Inhibition of angiotensin II type 1 receptor agonistic autoantibodies by direct binding does not impact reduced uterine perfusion pressure offspring birthweight and blood pressure at adulthood.Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2023 Jun;5(6):100945. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2023.100945. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2023. PMID: 36990181 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of tolerance development to morphine in rats prenatally exposed to morphine, methadone, and buprenorphine.J Biomed Sci. 2010 Jun 7;17(1):46. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-17-46. J Biomed Sci. 2010. PMID: 20529288 Free PMC article.
-
NTP technical report on the toxicity studies of Dibutyl Phthalate (CAS No. 84-74-2) Administered in Feed to F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice.Toxic Rep Ser. 1995 Apr;30:1-G5. Toxic Rep Ser. 1995. PMID: 12209194
-
Maternal high-fat diet acts on the brain to induce baroreflex dysfunction and sensitization of angiotensin II-induced hypertension in adult offspring.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 May 1;314(5):H1061-H1069. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00698.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 26. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29373045 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Obesity Human Soluble Prorenin Receptor Expressed in Adipose Tissue Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Endothelial Function in Obese Female Mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 9:2024.01.12.575451. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.12.575451. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38260688 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Obese Male Mice Exposed to Early Life Stress Display Sympathetic Activation and Hypertension Independent of Circulating Angiotensin II.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Jan 2;13(1):e029511. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.029511. Epub 2023 Dec 29. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38156515 Free PMC article.
-
Limited bedding and nesting increases ethanol drinking in female rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2024 Jun;239:173756. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2024.173756. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2024. PMID: 38555037 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in animal models of prenatal opioid exposure.Trends Neurosci. 2024 May;47(5):367-382. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2024.03.005. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Trends Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38614891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fetal and Infant Effects of Maternal Opioid Use during Pregnancy: A Literature Review including Clinical, Toxicological, Pharmacogenomic, and Epigenetic Aspects for Forensic Evaluation.Children (Basel). 2024 Feb 23;11(3):278. doi: 10.3390/children11030278. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539313 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention NCfIPaC. Drug Overdose. 2022; https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/deaths/index.html. Accessed October, 2022.
-
- Prevention CfDCa. Pregnancy. 2021; https://www.cdc.gov/pregnancy/opioids/data.html. Accessed October 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

