Identification and Characterization of Alveolar and Recruited Lung Macrophages during Acute Lung Inflammation
- PMID: 37042701
- PMCID: PMC10192112
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200694
Identification and Characterization of Alveolar and Recruited Lung Macrophages during Acute Lung Inflammation
Abstract
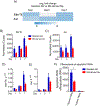
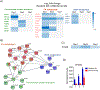
To precisely identify mouse resident alveolar macrophages (AMs) and bone marrow (BM)-derived macrophages, we developed a technique to separately label AMs and BM-derived macrophages with a fluorescent lipophilic dye followed by FACS. We showed that this technique overcomes issues in cell identification related to dynamic shifts in cell surface markers that occurs during lung inflammation. We then used this approach to track macrophage subsets at different time points after intratracheal (i.t.) instillation of Escherichia coli LPS. By isolating BM-derived macrophages and AMs, we demonstrated that BM-derived macrophages were enriched in expression of genes in signal transduction and immune system activation pathways whereas resident AMs were enriched in cellular processes, such as lysosome/phagosome pathways, efferocytosis, and metabolic pathways related to fatty acids and peroxisomes. Taken together, these data indicate that more accurate identification of macrophage origin can result in improved understanding of differential phenotypes and functions between AMs and BM-derived macrophages in the lungs.
Copyright © 2023 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures






References
-
- Koay MA, Gao X, Washington MK, Parman KP, Sadikot RT, Blackwell TS, and Christman JW. 2002. Macrophages are necessary for maximal nuclear factor-kappaB activation in response to endotoxin. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol 26: 572–578. - PubMed
-
- Blackwell TS, Lancaster LH, Blackwell TR, Venkatakrishnan A, abd Christman JW. 1999. Differential NF-kappaB activation after intratracheal endotoxin. Am. J. Physiol 277: L823–830. - PubMed
-
- Xue J, Schmidt SV, Sander J, Draffehn A, Krebs W, Quester I, De Nardo D, Gohel TD, Emde M, Schmidleithner L, Ganesan H, Nino-Castro A, Mallmann MR, Labzin L, Theis H, Kraut M, Beyer M, Latz E, Freeman TC, Ulas T, and Schultze JL. 2014. Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals a spectrum model of human macrophage activation. Immunity 40: 274–288. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto D, Chow A, Noizat C, Teo P, Beasley MB, Leboeuf M, Becker CD, See P, Price J, Lucas D, Gteter M, Mortha A, Boyer SW, Forsberg EC, Tanaka M, Van Rooijen N, Carcia-Saste A, Stanley ER, Ginhoux F, Frenette PS, and Merad M. 2013. Tissue-resident macrophages self-maintain locally throughout adult life with minimal contribution from circulating monocytes. Immunity 38: 792–804. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

