Alemtuzumab and CXCL9 levels predict likelihood of sustained engraftment after reduced-intensity conditioning HCT
- PMID: 37042921
- PMCID: PMC10368780
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009478
Alemtuzumab and CXCL9 levels predict likelihood of sustained engraftment after reduced-intensity conditioning HCT
Abstract
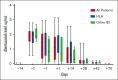
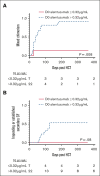
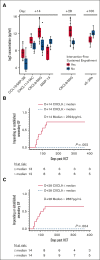
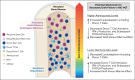
Overall survival after reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) using alemtuzumab, fludarabine, and melphalan is associated with high rates of mixed chimerism (MC) and secondary graft failure (GF). We hypothesized that peritransplantation alemtuzumab levels or specific patterns of inflammation would predict these risks. We assessed samples from the Bone Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network 1204 (NCT01998633) to study the impact of alemtuzumab levels and cytokine patterns on MC and impending or established secondary GF (defined as donor chimerism <5% after initial engraftment and/or requirement of cellular intervention). Thirty-three patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (n = 25) and other IEIs (n = 8) who underwent HCTs with T-cell-replete grafts were included. Patients with day 0 alemtuzumab levels ≤0.32 μg/mL had a markedly lower incidence of MC, 14.3%, vs 90.9% in patients with levels >0.32 μg/mL (P = .008). Impending or established secondary GF was only observed in patients with day 0 alemtuzumab levels >0.32 μg/mL (P = .08). Unexpectedly, patients with impending or established secondary GF had lower CXCL9 levels. The cumulative incidence of impending or established secondary GF in patients with a day 14+ CXCL9 level ≤2394 pg/mL (day 14+ median) was 73.6% vs 0% in patients with a level >2394 pg/mL (P = .002). CXCL9 levels inversely correlated with alemtuzumab levels. These data suggest a model in which higher levels of alemtuzumab at day 0 deplete donor T cells, inhibit the graft-versus-marrow reaction (thereby suppressing CXCL9 levels), and adversely affect sustained engraftment in the nonmyeloablative HCT setting. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01998633.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: C.E.A. is on the advisory board for Sobi, Atara Biotherapeutics, and Electra Therapeutics. M.B.J. is a consultant for Sobi and received research funding from Sobi. K.L.M. is on the advisory board of Sobi. J.A.C. is a Consultant for X4 Consultancy and is on the advisory board for Sobi and Horizon. P.R. is a consultant for Sobi. C.M.B. owns stock in Mana Therapeutics, Cabaletta Bio, Catamaran Bio, Repertoire Immune Medicine, and Neximmune, is a Data and Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) member for Sobi, and is on the ad hoc advisory board for BMS and Pfizer. S.S. is on the advisory board for Janssen Pharma Inc, Graphite Bio, and Bristol Myer Squibb, is a consultant for California Institute of Regenerative Medicine and on DSMB for Aruvant. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest. A.Z-L received consulting fees from Sobi.
Figures



References
-
- Marsh RA, Vaughn G, Kim MO, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning significantly improves survival of patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2010;116(26):5824–5831. - PubMed
-
- Cooper N, Rao K, Gilmour K, et al. Stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood. 2006;107(3):1233–1236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

