Diagnostics and Prevention of Occupational Allergy in Hairdressers
- PMID: 37043158
- PMCID: PMC10209293
- DOI: 10.1007/s11882-023-01076-z
Diagnostics and Prevention of Occupational Allergy in Hairdressers
Abstract
Purpose of review: This study aims to provide an overview on current knowledge on occupational allergic diseases in hairdressers and up-to-date perspectives of prevention.
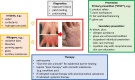
Recent findings: Hand eczema (dermatitis) is common in hairdressers, often caused by contact allergy to one or multiple small molecules (haptens) used, e.g., for dyeing, bleaching, and waving/relaxing or by ancillary substances such as preservatives. Hairdressers, compared to other patch-tested patients, have an up to fivefold increased risk to be found sensitized, e.g., against p-phenylenediamine, ammonium persulfate, and glyceryl thioglycolate. Some of these small molecules may induce respiratory sensitization causing allergic rhinitis and/or asthma, notably persulfate salts. Occupational hazards in hairdressing are well described. This knowledge needs to be put into use for risk reduction, mainly by substitution of allergenic ingredients by less allergenic ones, education, and use of ventilation and suitable single-use gloves.
Keywords: Asthma; Hair cosmetics; Hairdressers; Occupational diseases; Skin diseases; Workers’ health.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
W. Uter has accepted research funds from the IDEA project (IFRA,
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Results of patch test in hairdressers examined in the institute of occupational medicine in Łódź].Med Pr. 2009;60(6):459-67. Med Pr. 2009. PMID: 20187494 Polish.
-
Contact allergy to ingredients of hair cosmetics in female hairdressers and female consumers-An update based on IVDK data 2013-2020.Contact Dermatitis. 2023 Sep;89(3):161-170. doi: 10.1111/cod.14363. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Contact Dermatitis. 2023. PMID: 37315639
-
[Occupational contact dermatitis in hairdressers].Med Pr. 2009;60(5):377-82. Med Pr. 2009. PMID: 19999041 Polish.
-
Systematic review on skin adverse effects of important hazardous hair cosmetic ingredients with a focus on hairdressers.Contact Dermatitis. 2023 Feb;88(2):93-108. doi: 10.1111/cod.14236. Epub 2022 Oct 28. Contact Dermatitis. 2023. PMID: 36254351
-
Differences between hairdressers and consumers in skin exposure to hair cosmetic products: A review.Contact Dermatitis. 2022 May;86(5):333-343. doi: 10.1111/cod.14055. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Contact Dermatitis. 2022. PMID: 35088418 Review.
Cited by
-
Changing human hair fibre colour and shape from the follicle.J Adv Res. 2024 Oct;64:45-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.11.013. Epub 2023 Nov 13. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37967812 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Patterns and Risk Factors of Occupational Contact Dermatitis in Hairdressers: A Questionnaire-based Cross-sectional Study.Ann Dermatol. 2025 Jun;37(3):162-168. doi: 10.5021/ad.25.019. Ann Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40432365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Symanzik C, Weinert P, Babić Ž, Hallmann S, Havmose MS, Johansen JD, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and ethyl cyanoacrylate contained in cosmetic glues among hairdressers and beauticians who perform nail treatments and eyelash extension as well as hair extension applications: a systematic review. Contact Derm. 2022;86:480–492. doi: 10.1111/cod.14056. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials