Bioinspired Framework Catalysts: From Enzyme Immobilization to Biomimetic Catalysis
- PMID: 37043332
- PMCID: PMC10853941
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00879
Bioinspired Framework Catalysts: From Enzyme Immobilization to Biomimetic Catalysis
Abstract
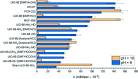
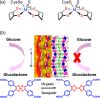
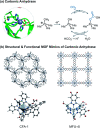
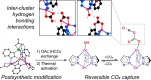
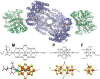
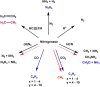
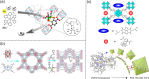
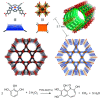
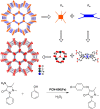
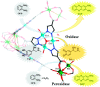
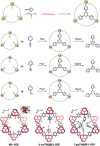
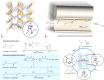
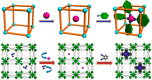
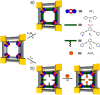
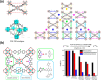
Enzymatic catalysis has fueled considerable interest from chemists due to its high efficiency and selectivity. However, the structural complexity and vulnerability hamper the application potentials of enzymes. Driven by the practical demand for chemical conversion, there is a long-sought quest for bioinspired catalysts reproducing and even surpassing the functions of natural enzymes. As nanoporous materials with high surface areas and crystallinity, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) represent an exquisite case of how natural enzymes and their active sites are integrated into porous solids, affording bioinspired heterogeneous catalysts with superior stability and customizable structures. In this review, we comprehensively summarize the advances of bioinspired MOFs for catalysis, discuss the design principle of various MOF-based catalysts, such as MOF-enzyme composites and MOFs embedded with active sites, and explore the utility of these catalysts in different reactions. The advantages of MOFs as enzyme mimetics are also highlighted, including confinement, templating effects, and functionality, in comparison with homogeneous supramolecular catalysts. A perspective is provided to discuss potential solutions addressing current challenges in MOF catalysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



















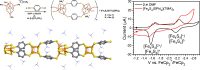



















References
-
- Dawson J. H.; Sono M. Cytochrome P-450 and Chloroperoxidase: Thiolate-Ligated Heme Enzymes. Spectroscopic Determination of Their Active-Site Structures and Mechanistic Implications of Thiolate Ligation. Chem. Rev. 1987, 87, 1255–1276. 10.1021/cr00081a015. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

