Measurements of fetal dose with Mevion S250i proton therapy system with HYPERSCAN
- PMID: 37043346
- PMCID: PMC10161065
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13957
Measurements of fetal dose with Mevion S250i proton therapy system with HYPERSCAN
Abstract
Purpose: To characterize potential dose to the fetus for all modes of delivery (dynamic adaptive aperture, static adaptive aperture, and no adaptive aperture) for the Mevion S250i Proton Therapy System with HYPERSCAN and compare the findings with those of other available proton systems.
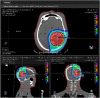
Materials and methods: Fetal dose measurements were performed for all three modes of dose delivery on the Mevion S250i Proton therapy system with HYPERSCAN (static aperture, dynamic aperture and uncollimated). Standard treatment plans were created in RayStation for a left-sided brain lesion treated with a vertex field, a left lateral field, and a posterior field. Measurements were performed using WENDI and the RANDO with the detector placed at representative locations to mimic the growth and movement of the fetus at different gestational stages.
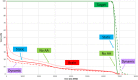
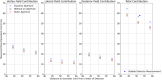
Results: The fetal dose measurements varied with fetus position and the largest measured dose was 64.7 μSv per 2 Gy (RBE) fraction using the dynamic aperture. The smallest estimated fetal dose was 45.0 μSv per 2 Gy (RBE) at the base of the RANDO abdomen (47 cm from isocenter to the outer width of WENDI and 58.5 cm from the center of the WENDI detector) for the static aperture delivery. The vertex fields at all depths had larger contributions to the total dose than the other two and the dynamic aperture plans resulted in the highest dose measured for all depths.
Conclusion: The reported doses are lower than reported doses using a double-scattering system. This work suggests that avoiding vertex fields and using the static aperture will help minimize dose to the fetus.
Keywords: fetal dose; scanning beam proton therapy.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of The American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no Conflicts of Interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dosimetric evaluation of dose shaping by adaptive aperture and its impact on plan quality.Med Dosim. 2024 Spring;49(1):30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2023.10.011. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Med Dosim. 2024. PMID: 38087750
-
Performance evaluation of adaptive aperture's static and dynamic collimation in a compact pencil beam scanning proton therapy system: A dosimetric comparison study for multiple disease sites.Med Dosim. 2021 Summer;46(2):179-187. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2020.11.001. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Med Dosim. 2021. PMID: 33279369
-
Characterization of penumbra sharpening and scattering by adaptive aperture for a compact pencil beam scanning proton therapy system.Med Phys. 2021 Apr;48(4):1508-1519. doi: 10.1002/mp.14771. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33580550
-
Exploring the feasibility of a clinical proton beam with an adaptive aperture for pre-clinical research.Br J Radiol. 2019 Mar;92(1095):20180446. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180446. Epub 2018 Nov 7. Br J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30362812 Free PMC article.
-
EURADOS REM-COUNTER INTERCOMPARISON AT MAASTRO PROTON THERAPY CENTRE: COMPARISON WITH LITERATURE DATA.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2022 Oct 16;198(19):1471-1475. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncac189. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2022. PMID: 36138419 Review.
Cited by
-
Out-of-field dose assessment for pencil beam scanning proton radiotherapy versus photon radiotherapy for breast cancer in pregnant women.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2025 Feb 4;33:100721. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2025.100721. eCollection 2025 Jan. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40123769 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and opportunities for proton therapy during pregnancy.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2024 Apr;103(4):767-774. doi: 10.1111/aogs.14645. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2024. PMID: 37491770 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal dose assessment in a pregnant patient with brain tumor: A comparative study of proton PBS and 3DCRT/VMAT radiation therapy techniques.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Aug;25(8):e14394. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14394. Epub 2024 Jun 17. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38887816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Association of Proton Therapy . Accessed 07/21/2022, 2022. https://www.proton‐therapy.org
-
- Shrestha S, Newhauser WD, Donahue WP, Perez‐Andujar AA. Stray neutron radiation exposures from proton therapy: physics‐based analytical models of neutron spectral fluence, kerma and absorbed dose. Phys Med Biol. 2022;67(12):125019. - PubMed
-
- Stovall M, Blackwell CR, Cundiff J, et al. Fetal dose from radiotherapy with photon beams: report of AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group No. 36. Med Phys. 1995;22(1):63‐82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

