Decoding the molecular crosstalk between grafted stem cells and the stroke-injured brain
- PMID: 37043353
- PMCID: PMC10562513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112353
Decoding the molecular crosstalk between grafted stem cells and the stroke-injured brain
Erratum in
-
Decoding the molecular crosstalk between grafted stem cells and the stroke-injured brain.Cell Rep. 2023 Aug 29;42(8):113002. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113002. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37561627 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
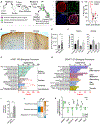
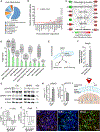
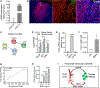
Stem cell therapy shows promise for multiple disorders; however, the molecular crosstalk between grafted cells and host tissue is largely unknown. Here, we take a step toward addressing this question. Using translating ribosome affinity purification (TRAP) with sequencing tools, we simultaneously decode the transcriptomes of graft and host for human neural stem cells (hNSCs) transplanted into the stroke-injured rat brain. Employing pathway analysis tools, we investigate the interactions between the two transcriptomes to predict molecular pathways linking host and graft genes; as proof of concept, we predict host-secreted factors that signal to the graft and the downstream molecular cascades they trigger in the graft. We identify a potential host-graft crosstalk pathway where BMP6 from the stroke-injured brain induces graft secretion of noggin, a known brain repair factor. Decoding the molecular interplay between graft and host is a critical step toward deciphering the molecular mechanisms of stem cell action.
Keywords: BMP6; CP: Neuroscience; CP: Stem cell research; NOG; RNA-seq; TRAP; mechanism; stem cell; stroke; transcriptome; transplant.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Steinberg GK, Kondziolka D, Wechsler LR, Lunsford LD, Coburn ML, Billigen JB, Kim AS, Johnson JN, Bates D, King B, et al. (2016). Clinical outcomes of transplanted modified bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in stroke: a phase 1/2a study. Stroke 47, 1817–1824. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.012995. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Horie N, Pereira MP, Niizuma K, Sun G, Keren-Gill H, Encarnacion A, Shamloo M, Hamilton SA, Jiang K, Huhn S, et al. (2011). Transplanted stem cell-secreted vascular endothelial growth factor effects poststroke recovery, inflammation, and vascular repair. Stem Cells 29, 274–285. 10.1002/stem.584. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

