Standing genetic variation fuels rapid evolution of herbicide resistance in blackgrass
- PMID: 37043536
- PMCID: PMC10120058
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2206808120
Standing genetic variation fuels rapid evolution of herbicide resistance in blackgrass
Abstract
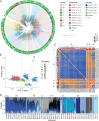
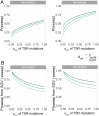
Repeated herbicide applications in agricultural fields exert strong selection on weeds such as blackgrass (Alopecurus myosuroides), which is a major threat for temperate climate cereal crops. This inadvertent selection pressure provides an opportunity for investigating the underlying genetic mechanisms and evolutionary processes of rapid adaptation, which can occur both through mutations in the direct targets of herbicides and through changes in other, often metabolic, pathways, known as non-target-site resistance. How much target-site resistance (TSR) relies on de novo mutations vs. standing variation is important for developing strategies to manage herbicide resistance. We first generated a chromosome-level reference genome for A. myosuroides for population genomic studies of herbicide resistance and genome-wide diversity across Europe in this species. Next, through empirical data in the form of highly accurate long-read amplicons of alleles encoding acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACCase) and acetolactate synthase (ALS) variants, we showed that most populations with resistance due to TSR mutations-23 out of 27 and six out of nine populations for ACCase and ALS, respectively-contained at least two TSR haplotypes, indicating that soft sweeps are the norm. Finally, through forward-in-time simulations, we inferred that TSR is likely to mainly result from standing genetic variation, with only a minor role for de novo mutations.
Keywords: Alopecurus myosuroides; blackgrass; herbicide resistance; rapid adaptation.
Conflict of interest statement
J.L. and A.P. are employees of BASF, which manufactures and sells herbicides. D.W. holds equity in Computomics, which advises breeders. D.W. advises KWS SE, a plant breeder and seed producer. All other authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Moss S. R., Perryman S. A. M., Tatnell L. V., Managing herbicide-resistant blackgrass (Alopecurus Myosuroides): Theory and practice. Weed Technol. 21, 300–309 (2007).
-
- Rosenhauer M., Jaser B., Felsenstein F. G., Petersen J., Development of target-site resistance (TSR) in Alopecurus myosuroides in Germany between 2004 and 2012. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 120, 179–187 (2013).
-
- Xu H., et al. , Mutations at codon position 1999 of acetyl-CoA carboxylase confer resistance to ACCase-inhibiting herbicides in Japanese foxtail (Alopecurus japonicus). Pest Manag. Sci. 70, 1894–1901 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

