An RNA-based system to study hepatitis B virus replication and evaluate antivirals
- PMID: 37043562
- PMCID: PMC10096565
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg6265
An RNA-based system to study hepatitis B virus replication and evaluate antivirals
Abstract
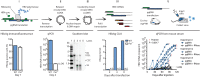
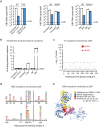
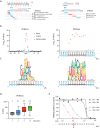
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects an estimated 300 million people, and standard treatments are rarely curative. Infection increases the risk of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, and consequently, nearly 1 million people die each year from chronic hepatitis B. Tools and approaches that bring insights into HBV biology and facilitate the discovery and evaluation of antiviral drugs are in demand. Here, we describe a method to initiate the replication of HBV, a DNA virus, using synthetic RNA. This approach eliminates contaminating background signals from input virus or plasmid DNA that plagues existing systems and can be used to study multiple stages of HBV replication. We further demonstrate that this method can be uniquely applied to identify sequence variants that confer resistance to antiviral drugs.
Figures

References
-
- M. Nassal, HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 64, 1972–1984 (2015). - PubMed
-
- P. A. Revill, F. V. Chisari, J. M. Block, M. Dandri, A. J. Gehring, H. Guo, J. Hu, A. Kramvis, P. Lampertico, H. L. A. Janssen, M. Levrero, W. Li, T. J. Liang, S.-G. Lim, F. Lu, M. C. Penicaud, J. E. Tavis, R. Thimme; Members of the ICE-HBV Working Groups; ICE-HBV Stakeholders Group Chairs; ICE-HBV Senior Advisors, F. Zoulim, A global scientific strategy to cure hepatitis B. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 4, 545–558 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, Global progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections, 2021 (World Health Organization, 2021); www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240027077 .
-
- H. Yan, G. Zhong, G. Xu, W. He, Z. Jing, Z. Gao, Y. Huang, Y. Qi, B. Peng, H. Wang, L. Fu, M. Song, P. Chen, W. Gao, B. Ren, Y. Sun, T. Cai, X. Feng, J. Sui, W. Li, Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 1, e00049 (2012). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

