Cerebral phaeohyphomycosis at a tertiary healthcare center in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 37045456
- PMCID: PMC10155477
- DOI: 10.17712/nsj.2023.2.20220118
Cerebral phaeohyphomycosis at a tertiary healthcare center in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Objectives: To report cases of cerebral phaeohyphomycosis at a tertiary hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Phaeohyphomycetes are a widely distributed group of fungi whose cell walls contain 1,8 dihydroxynaphthalene-melanin. Cerebral infections caused by these fungi are uncommon and primarily associated with neurotrophic phaeohyphomycetes.
Methods: In January of 2020 we looked back to identify cases of culture-positive cerebral phaeohyphomycosis from our medical records at King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Data on demographics, potential risk factors, clinical presentation, treatment, and outcomes were analyzed.
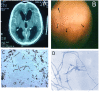
Results: Twelve cases of cerebral phaeohyphomycosis were identified, of which 4 were caused by Rhinocladiella mackenziei and the other 8 were caused by various phaeohyphomycetes. There were 2 cases caused by Neoscytalidium dimidiatum, and one case each caused by the following: Acrophialophora fusispora, Chaetomium atrobrunneum, Exophiala dermatitidis, Exerohilum rostratum, Fonsecaea pedrosoi, and Cladophialophora bantiana. Most patients (10 of 12) had underlying immunosuppression. R. mackenziei caused a brain-only infection manifesting as abscess formation. Four patients survived for more than a year after therapy. Surgical evacuation and triazole therapy with posaconazole or itraconazole, alone or in combination with other antifungal agents, were associated with success.
Conclusion: Cerebral phaeohyphomycosis is an uncommon fungal infection that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and is associated with poor prognosis. R. mackenziei is the most prevalent fungus in our facility and has been linked to a universal mortality.
Copyright: © Neurosciences.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Abdely, HM. Phaeohyphomycosis: A Dark Question Mark in Clinical Disease. J Invasive Fungal Infect 2009; 3: 82–88.
-
- Ajello L, Georg LK, Steigbigel RT, Wang CJ.. A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by a new species of Phialophora. Mycologia 1974; 66: 490–498. - PubMed
-
- Jabeen K, Farooqi J, Zafar A, Jamil B, Mahmood SF, Ali F, et al. . Rhinocladiella mackenziei as an emerging cause of cerebral Phaeohyphomycosis in Pakistan: a case series. Clin Infect Dis 2011; 52: 213–217. - PubMed
-
- Mohammadi R, Mohammadi A, Ashtari F, Khorvash F, Hakamifard A, Vaezi A, et al. . Cerebral Phaeohyphomycosis due to Rhinocladiella mackenziei in Persian Gulf region: A case and review. Mycoses 2018; 61: 261–265. - PubMed
-
- Hardman N, Young N, Hobson R, Sandoe J, Wellbery-Smith M, Thomson S, et al. . Prolonged survival after disseminated Rhinocladiella infection treated with surgical excision and posaconazole. Transpl Infect Dis 2020; 22: e13264. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
