Unified access to up-to-date residue-level annotations from UniProtKB and other biological databases for PDB data
- PMID: 37045837
- PMCID: PMC10097656
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-023-02101-6
Unified access to up-to-date residue-level annotations from UniProtKB and other biological databases for PDB data
Abstract
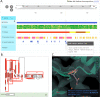
More than 61,000 proteins have up-to-date correspondence between their amino acid sequence (UniProtKB) and their 3D structures (PDB), enabled by the Structure Integration with Function, Taxonomy and Sequences (SIFTS) resource. SIFTS incorporates residue-level annotations from many other biological resources. SIFTS data is available in various formats like XML, CSV and TSV format or also accessible via the PDBe REST API but always maintained separately from the structure data (PDBx/mmCIF file) in the PDB archive. Here, we extended the wwPDB PDBx/mmCIF data dictionary with additional categories to accommodate SIFTS data and added the UniProtKB, Pfam, SCOP2, and CATH residue-level annotations directly into the PDBx/mmCIF files from the PDB archive. With the integrated UniProtKB annotations, these files now provide consistent numbering of residues in different PDB entries allowing easy comparison of structure models. The extended dictionary yields a more consistent, standardised metadata description without altering the core PDB information. This development enables up-to-date cross-reference information at the residue level resulting in better data interoperability, supporting improved data analysis and visualisation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
- BB/V004247/1, PI:Sameer Velankar/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- BB/V004247/1, PI:Sameer Velankar/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- BB/V004247/1, PI:Sameer Velankar/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- BB/V004247/1, PI:Sameer Velankar/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- BB/V004247/1, PI:Sameer Velankar/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- BB/V004247/1, PI:Sameer Velankar/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- DBI-2019297, PI: S.K. Burley/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- DBI-2019297, PI: S.K. Burley/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- DBI-2019297, PI: S.K. Burley)/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- DBI-2019297, PI: S.K. Burley/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- DBI-2019297, PI: S.K. Burley/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- DBI-2019297, PI: S.K. Burley/NSF | National Science Board (NSB)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

