The hyperexcitability of laterodorsal tegmentum cholinergic neurons accompanies adverse behavioral and cognitive outcomes of prenatal stress
- PMID: 37045899
- PMCID: PMC10097720
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-33016-2
The hyperexcitability of laterodorsal tegmentum cholinergic neurons accompanies adverse behavioral and cognitive outcomes of prenatal stress
Abstract
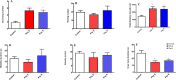
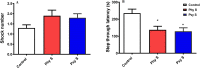
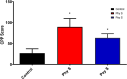
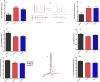
Exposure to prenatal stress (PS) leads to the offspring's vulnerability towards the development of cognitive and behavioral disorders. Laterodorsal tegmentum (LDT) is a part of the brainstem cholinergic system that is believed to play a pivotal role in the stress-associated progression of anxiety, memory impairment, and addictive behaviors. In this study, we aimed to investigate the electrophysiological alterations of LDT cholinergic neurons and its accompanied behavioral and cognitive outcomes in the offspring of mice exposed to physical or psychological PS. Swiss Webster mice were exposed to physical or psychological stress on the tenth day of gestation. Ex vivo investigations in LDT brain slices of adolescent male offspring were performed to evaluate the effects of two stressor types on the activity of cholinergic neurons. Open field test, elevated plus maze, passive avoidance test, and conditioned place preference were conducted to assess behavioral and cognitive alterations in the offspring. The offspring of both physical and psychological PS-exposed mice exhibited increased locomotor activity, anxiety-like behavior, memory impairment, and preference to morphine. In both early- and late-firing cholinergic neurons of the LDT, stressed groups demonstrated higher firing frequency, lower adaptation ratio, decreased action potential threshold, and therefore increased excitability compared to the control group. The findings of the present study suggest that the hyperexcitability of the cholinergic neurons of LDT might be involved in the development of PS-associated anxiety-like behaviors, drug seeking, and memory impairment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Roshan-Milani S, Seyyedabadi B, Saboory E, Parsamanesh N, Mehranfard N. Prenatal stress and increased susceptibility to anxiety-like behaviors: role of neuroinflammation and balance between GABAergic and glutamatergic transmission. Stress. 2021;24:481–495. doi: 10.1080/10253890.2021.1942828. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

