Influencing factors and predictive model of postoperative infection in patients with primary hepatic carcinoma
- PMID: 37046206
- PMCID: PMC10099730
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-023-02713-7
Influencing factors and predictive model of postoperative infection in patients with primary hepatic carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to explore the risk factors for postoperative infection in patients with primary hepatic carcinoma (PHC), build a nomogram prediction model, and verify the model to provide a better reference for disease prevention, diagnosis and treatment.
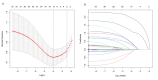
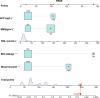
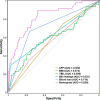
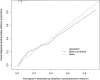
Methods: This single-center study included 555 patients who underwent hepatobiliary surgery in the Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery of Tianjin Third Central Hospital from January 2014 to December 2021, and 32 clinical indicators were selected for statistical analysis. In this study, Lasso logistic regression was used to determine the risk factors for infection after liver cancer resection, establish a predictive model, and construct a visual nomogram. The consistency index (C-index), calibration curve, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve were used for internal validation, and decision curve analysis (DCA) was used to analyze the clinical applicability of the predictive model. The bootstrap method was used for intramodel validation, and the C-index was calculated to assess the model discrimination.
Results: Among the 555 patients, 279 patients met the inclusion criteria, of whom 48 had a postoperative infection, with an incidence rate of 17.2%. Body mass index (BMI) (P = 0.022), alpha-fetoprotein (P = 0.023), total bilirubin (P = 0.016), intraoperative blood loss (P < 0.001), and bile leakage (P < 0.001) were independent risk factors for infection after liver cancer surgery. The nomogram was constructed and verified to have good discriminative and predictive ability. DCA showed that the model had good clinical applicability. The C-index value verified internally by the bootstrap method results was 0.818.
Conclusion: Postoperative infection in patients undergoing hepatectomy may be related to risk factors such as BMI, preoperative AFP level, TBIL level, intraoperative blood loss and bile leakage. The prediction model of the postoperative infection nomogram established in this study can better predict and estimate the risk of postoperative infection in patients undergoing hepatectomy.
Keywords: Nomogram; Postoperative infection; Predictive model; Primary hepatic carcinoma; Risk factors.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Risk factor analysis on body mass rebound after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and establishment of a nomogram prediction model].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Oct 25;25(10):913-920. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441530-20220418-00159. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36245117 Chinese.
-
[Risk factor analysis on anastomotic leakage after laparoscopic surgery in rectal cancer patient with neoadjuvant therapy and establishment of a nomogram prediction model].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Aug 25;22(8):748-754. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0274.2019.08.009. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31422613 Chinese.
-
Establishment and validation of a predictive nomogram for severe pleural effusion in liver cancer patients after hepatectomy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Mar 8;103(10):e36556. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036556. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38457588 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram for predicting post-hepatectomy liver failure in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma based on spleen-volume-to-platelet ratio.Asian J Surg. 2023 Jan;46(1):399-404. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2022.05.001. Epub 2022 May 20. Asian J Surg. 2023. PMID: 35599113
-
Applying LASSO logistic regression for the prediction of biliary complications after ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation in patients with end-stage hepatic alveolar echinococcosis.Eur J Med Res. 2024 May 29;29(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01898-1. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38812045 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a postoperative pulmonary infection prediction model for patients with primary hepatic carcinoma.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Jul 15;15(7):1241-1252. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i7.1241. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37546550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao P, Jiang DM, Xian LF, Lin JS, Liu DH, Zhang LJ, Yu HP, Cao GW. Mortality analysis of primary liver cancer in the mainland of China from 2004 to 2018. Shanghai J Prev Med. 2021;33(10):881–6.
-
- General Office of National Health Commission Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2022 edition) J Clin Hepatol. 2022;38(2):288–303.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- KJ20134/Science and technology talent training project of Tianjin Health Commission
- TJWJ2021ZD003/The Key Research Project of Tianjin Health Commission
- TJYXZDXK-047A/Tianjin Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Construction Project
- 21JCZDJC01050/Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin Science and Technology Bureau
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

