Examining the effects of student-centered flipped classroom in physiology education
- PMID: 37046277
- PMCID: PMC10091629
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-023-04166-8
Examining the effects of student-centered flipped classroom in physiology education
Abstract
Background: The flipped classroom approach has gained increasing popularity in medical education. Physiology is a basic medical course that studies the phenomena and laws of human life activities, and is a crucial link course connecting preclinical courses and clinical courses. However, there is a paucity of data showing the effectiveness of the flipped classroom model for the entirety of physiology course in medical undergraduate students.
Method: 131 sophomore students with clinical medicine major at Harbin Medical University were recruited and they were randomly allocated into two groups: the control group which was subjected to traditional lecture teaching (n = 69), and the experimental group which was subjected to flipped classroom teaching (n = 62). To assess the effect of flipped teaching, the usual performance and final exam scores were used to evaluate the physiology learning effectiveness of students. The correlation between the usual performance and final exam scores by Pearson method was also conducted in the two teaching groups. After course completion, an anonymous questionnaire survey was conducted among the subjects of flipped classroom group to assess students' opinion regarding the flipped classroom teaching.
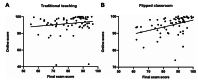
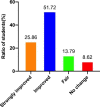
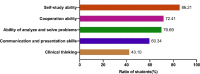
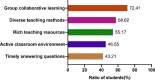
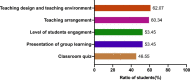
Results: Our results showed that the usual performance and final exam scores of students in the flipped classroom were both significantly higher than that in the traditional teaching class (P < 0.05). Moreover, our results also showed that the usual performance of students was significantly correlated with the final exam scores in the flipped classroom (r = 0.3945, P < 0.01), but not in the traditional teaching group (r = 0.1522, P = 0.2119). The results of questionnaire survey showed that 77.58% of the students believed flipped classroom teaching improved their knowledge acquisition. 70%~86% of students perceived that flipped classroom enhanced their learning abilities, including self-study ability, collaborative learning and problem-solving skills, and clinical thinking ability. In addition, about 60% of students acknowledged the teaching design and teaching environment, more students' engagement and presentation of group learning in the flipped classroom.
Conclusion: The flipped classroom teaching significantly improved students' learning effectiveness in physiology course, as indicated by final exam score and usual performance. It also promoted higher-order ability-set acquisition and allowed a rationalized formative evaluation system.
Keywords: Flipped classroom; Online teaching; Physiology education; Teaching model.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

