Potentialities and limitations of Interprofessional Education during graduation: a systematic review and thematic synthesis of qualitative studies
- PMID: 37046287
- PMCID: PMC10099638
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-023-04211-6
Potentialities and limitations of Interprofessional Education during graduation: a systematic review and thematic synthesis of qualitative studies
Abstract
Background: Rapid demographic, epidemiological, technological, cultural/behavioural, and educational transitions, as they become more complex, demand new integrated and complementary professional skills and abilities. Interprofessional Education (IPE) is a promising alternative to deal with these changes, especially in courses in the health area. This systematic review was to explore the potentialities and limitations of IPE, from the perspective of undergraduate students, through a thematic synthesis of qualitative studies.
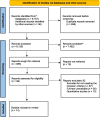
Methods: A thematic synthesis of qualitative studies was conducted. The question elaborated for this review was: "What is the impact of interprofessional education on the teaching and learning of students in the health area inserted in Higher Education Institutions?". The search strategy was performed in the electronic databases PubMed, Latin American and Caribbean Literature in Health Sciences (LILACS), Cochrane Library, and Scientific Electronic Library Online (SciELO). In addition, searches were carried out in grey literature on the ERIC platforms, ProQuest Disserts and Theses, and Academic Google. The assessment of the quality of the studies was carried out using the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme tool. Data were summarized through thematic synthesis. From the databases, 8,793 studies were identified. After standardized filters procedures, critical summaries, and assessment of relevance to the eligibility criteria, 14 articles were included.
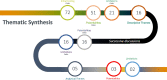
Results: The synthesis of the studies revealed the potential of this teaching approach, arranged in three analytical themes: learning from each other and about them; the value of education and interprofessional practice; patient-centred health care. On the other hand, some limitations were also identified, such as barriers related to EIP; the difficulties related to teaching methodologies.
Conclusion: Overcoming the identified limitations can enhance the results of the IPE, in view of its impact on the education of students and on the health care of the population.
Keywords: Education; Interdisciplinary communication; Interprofessional education; Professional; Students.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of interprofessional education on the teaching and learning of higher education students: A systematic review.Nurse Educ Pract. 2021 Oct;56:103212. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2021.103212. Epub 2021 Sep 18. Nurse Educ Pract. 2021. PMID: 34571466
-
Sustainability of Interprofessional Education: Protocol for a Scoping Review.JMIR Res Protoc. 2024 Dec 9;13:e60763. doi: 10.2196/60763. JMIR Res Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39652377 Free PMC article.
-
Student and educator experiences of maternal-child simulation-based learning: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):14-26. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1694. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447004
-
What did first-year students experience during their interprofessional education? A qualitative analysis of e-portfolios.J Interprof Care. 2018 May;32(3):358-366. doi: 10.1080/13561820.2018.1427051. Epub 2018 Jan 24. J Interprof Care. 2018. PMID: 29364744
-
Mapping the interprofessional education landscape for students on rural clinical placements: an integrative literature review.Rural Remote Health. 2018 May;18(2):4336. doi: 10.22605/RRH4336. Epub 2018 May 4. Rural Remote Health. 2018. PMID: 29724107 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights of undergraduate health sciences students about a French interprofessional training initiative.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Mar 1;24(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05212-9. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38429678 Free PMC article.
-
Interprofessional education in cardiothoracic surgery: a narrative review.Front Surg. 2024 Sep 4;11:1467940. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1467940. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 39296347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interprofessional collaboration skills and motivation one year after an interprofessional educational intervention for undergraduate medical and nursing students.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Mar 11;24(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05262-z. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38468246 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a global partnership to adapt and deliver interprofessional education faculty training in Kenya during the COVID-19 pandemic: reporting on an innovative collaboration.J Interprof Care. 2024 Sep-Oct;38(5):942-946. doi: 10.1080/13561820.2024.2343829. Epub 2024 May 8. J Interprof Care. 2024. PMID: 38717763
-
The integration of psychology and medicine: an empirical study of curriculum reform from the perspective of China.Front Psychol. 2024 Sep 4;15:1469067. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1469067. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39295748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Framework for Action on Interprofessional Education & Collaborative Practice. Genebra: WHO; 2010. - PubMed
-
- Barr H. Interprofessional education: the genesis of a global movement. London: Centre for Advancement of Interprofessional Education; 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

