Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemorrhage in Infancy: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 37046488
- PMCID: PMC10093109
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13071270
Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemorrhage in Infancy: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
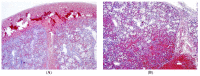
Acute idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage in infants (AIPHI) is a rare and quite low-described entity. Nowadays, pathophysiological mechanisms are poorly understood, although the lethality remains high. We present an autopsy case report of a 2-day-old male who developed respiratory distress and blood leakage from the endotracheal tube (ET) and suddenly died because of acute pulmonary hemorrhage. A postmortem examination and histological analysis were performed and are reported in this paper. Alveolar spaces were filled with red blood cells and hyaline membranes in all the examined samples. The absence of other findings led us to select a post-mortem diagnosis of AIPHI. To support our diagnosis, we conducted a systematic review of the updated scientific literature and found that only 61 cases have been reported. Most of them presented acute respiratory distress and bleeding from the upper airways with blood leakage from ET (9.83%), hemoptysis (52.45%), epistaxis (8.2%), and hematemesis (3.27%). The autopsy data revealed hemorrhages of the lower airways and hemosiderin-laden macrophages. The data from the scientific publications and our findings are essential to achieving a correct diagnosis. On these bases, we suggest autoptic criteria to achieve a post-mortem diagnosis of AIPHI.
Keywords: acute idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage in infants (AIPHI); autopsy; case report; forensic; lung histology; postmortem; pulmonary hemorrhage; sudden infant death syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemorrhage.2023 Feb 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Feb 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 32491447 Free Books & Documents.
-
Pulmonary hemorrhage in infancy: A 10-year single-center experience.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2018 Nov;53(11):1559-1564. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24142. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2018. PMID: 30125478
-
The frequency and significance of alveolar haemosiderin-laden macrophages in sudden infant death.Forensic Sci Int. 2009 May 30;187(1-3):51-7. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2009.02.016. Epub 2009 Mar 28. Forensic Sci Int. 2009. PMID: 19329265
-
Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis and alveolar hemorrhage syndrome: case report and review of the literature.S D J Med. 1995 Mar;48(3):79-85. S D J Med. 1995. PMID: 7740300 Review.
-
Sudden twin infant death on the same day: a case report and review of the literature.Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2013 Jun;9(2):225-30. doi: 10.1007/s12024-013-9429-3. Epub 2013 Mar 24. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23526355 Review.
Cited by
-
Traumatic Aneurysm Involving the Posterior Communicating Artery.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Jan 13;12(2):192. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12020192. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38255080 Free PMC article.
-
Sudden Death: A Practical Autopsy Approach to Unexplained Mediastinitis Due to Fatal Untreated Neck Infections-A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 May 30;14(11):1150. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14111150. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Apoptotic Caspase-3 Immunopositivity in Human Model of Asphyxial Death.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 2;26(7):3317. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073317. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244211 Free PMC article.
-
Interstitial Lung Disease in Neonates: A Long Road Is Being Paved.Children (Basel). 2023 May 23;10(6):916. doi: 10.3390/children10060916. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kher P. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. [(accessed on 1 February 2022)]. Hemorrhagic Disease of Newborn. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558994/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

