Optical Biopsy of Dysplasia in Barrett's Oesophagus Assisted by Artificial Intelligence
- PMID: 37046611
- PMCID: PMC10093622
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15071950
Optical Biopsy of Dysplasia in Barrett's Oesophagus Assisted by Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
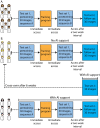
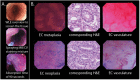
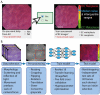
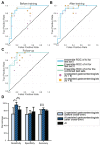
Optical biopsy in Barrett's oesophagus (BE) using endocytoscopy (EC) could optimize endoscopic screening. However, the identification of dysplasia is challenging due to the complex interpretation of the highly detailed images. Therefore, we assessed whether using artificial intelligence (AI) as second assessor could help gastroenterologists in interpreting endocytoscopic BE images. First, we prospectively videotaped 52 BE patients with EC. Then we trained and tested the AI pm distinct datasets drawn from 83,277 frames, developed an endocytoscopic BE classification system, and designed online training and testing modules. We invited two successive cohorts for these online modules: 10 endoscopists to validate the classification system and 12 gastroenterologists to evaluate AI as second assessor by providing six of them with the option to request AI assistance. Training the endoscopists in the classification system established an improved sensitivity of 90.0% (+32.67%, p < 0.001) and an accuracy of 77.67% (+13.0%, p = 0.020) compared with the baseline. However, these values deteriorated at follow-up (-16.67%, p < 0.001 and -8.0%, p = 0.009). Contrastingly, AI-assisted gastroenterologists maintained high sensitivity and accuracy at follow-up, subsequently outperforming the unassisted gastroenterologists (+20.0%, p = 0.025 and +12.22%, p = 0.05). Thus, best diagnostic scores for the identification of dysplasia emerged through human-machine collaboration between trained gastroenterologists with AI as the second assessor. Therefore, AI could support clinical implementation of optical biopsies through EC.
Keywords: Barrett’s dysplasia; computer-aided diagnosis; endocytoscopy; machine learning; medical training; surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
J.v.d.P., F.v.d.S. and P.d.W. have received research support from FUJIFILM and OLYMPUS that was not related to this project. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Machine Learning Creates a Simple Endoscopic Classification System that Improves Dysplasia Detection in Barrett's Oesophagus amongst Non-expert Endoscopists.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018 Aug 29;2018:1872437. doi: 10.1155/2018/1872437. eCollection 2018. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30245711 Free PMC article.
-
A new artificial intelligence system successfully detects and localises early neoplasia in Barrett's esophagus by using convolutional neural networks.United European Gastroenterol J. 2022 Jul;10(6):528-537. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12233. Epub 2022 May 6. United European Gastroenterol J. 2022. PMID: 35521666 Free PMC article.
-
AI analysis and modified type classification for endocytoscopic observation of esophageal lesions.Dis Esophagus. 2022 Sep 14;35(9):doac010. doi: 10.1093/dote/doac010. Dis Esophagus. 2022. PMID: 35292794
-
Artificial Intelligence in the Detection of Barrett's Esophagus: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Oct 26;15(10):e47755. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47755. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to Detect Early Neoplasia in Barrett's Esophagus: A Non-comparative Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 22;9:890720. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.890720. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35814747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Serag H.B., Naik A.D., Duan Z., Shakhatreh M., Helm A., Pathak A., Hinojosa-Lindsey M., Hou J., Nguyen T., Chen J., et al. Surveillance endoscopy is associated with improved outcomes of oesophageal adenocarcinoma detected in patients with Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut. 2016;65:1252–1260. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308865. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Munster S., Nieuwenhuis E., Weusten B.L., Herrero L.A., Bogte A., Alkhalaf A., Schenk B.E., Schoon E.J., Curvers W., Koch A.D., et al. Long-term outcomes after endoscopic treatment for Barrett’s neoplasia with radiofrequency ablation ± endoscopic resection: Results from the national Dutch database in a 10-year period. Gut. 2021;71:265–276. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322615. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

