KRAS Mutations Are Associated with Shortened Survival in Patients with Epithelioid Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
- PMID: 37046732
- PMCID: PMC10093256
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15072072
KRAS Mutations Are Associated with Shortened Survival in Patients with Epithelioid Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
Abstract
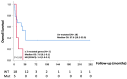
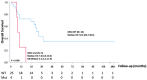
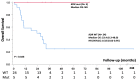
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is an aggressive malignancy of the pleural surface that includes three major histologic subtypes, epitheliod, sarcomatoid and biphasic. Epithelioid mesothelioma is usually associated with better prognosis. The genetic mechanisms driving MPM, the possible target mutations and the correlation with overall survival remain largely unsettled. We performed target exome sequencing in 29 cases of MPM aimed at identifying somatic mutations and, eventually, their correlation with phenotypic traits and prognostic significance. We found that KRAS mutations, occurring in 13.7% of cases, were associated with shortened median survival (7.6 versus 32.6 months in KRAS wild-type; p = 0.005), as it was the occurrence of any ≥3 mutations (7.6 versus 37.6 months; p = 0.049). Conversely, the presence of KDR single nucleotide polymorphism p.V297I (rs2305948) resulted in a favorable variable for survival (NR versus 23.4 months; p = 0.026). With the intrinsic limitations of a small number of cases and patient heterogeneity, results of this study contribute to the characterization of the mutation profile of MPM and the impact of selected somatic mutations, and possibly KDR polymorphism, on prognosis.
Keywords: KDR gene; KRAS mutation; MPM prognosis; epithelioid mesothelioma; pleural mesothelioma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Travis W.D., Brambilla E., Nicholson A.G., Yatabe Y., Austin J.H.M., Beasley M.B., Chirieac L.R., Dacic S., Duhig E., Flieder D.B., et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015;10:1243–1260. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000630. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Paajanen J., Laaksonen S., Ilonen I., Vehmas T., Mäyränpää M.I., Sutinen E., Kettunen E., Salo J.A., Räsänen J., Wolff H., et al. Clinical Features in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma With 5-Year Survival and Evaluation of Original Diagnoses. Clin. Lung Cancer. 2020;21:e633–e639. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2020.05.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer . IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Man: Asbestos. Volume 14. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 1977. pp. 1–106. - PubMed
-
- Sauter J.L., Dacic S., Galateau-Salle F., Attanoos R.L., Butnor K.J., Churg A., Husain A.N., Kadota K., Khoor A., Nicholson A.G., et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the pleura: Advances since the 2015 classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021;17:608–622. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.12.014. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous