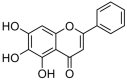
Baicalein as Promising Anticancer Agent: A Comprehensive Analysis on Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives
- PMID: 37046789
- PMCID: PMC10093079
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15072128
Baicalein as Promising Anticancer Agent: A Comprehensive Analysis on Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives
Abstract
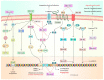
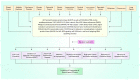
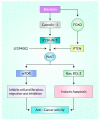
Despite significant therapeutic advancements for cancer, an atrocious global burden (for example, health and economic) and radio- and chemo-resistance limit their effectiveness and result in unfavorable health consequences. Natural compounds are generally considered safer than synthetic drugs, and their use in cancer treatment alone, or in combination with conventional therapies, is increasingly becoming accepted. Interesting outcomes from pre-clinical trials using Baicalein in combination with conventional medicines have been reported, and some of them have also undergone clinical trials in later stages. As a result, we investigated the prospects of Baicalein, a naturally occurring substance extracted from the stems of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi and Oroxylum indicum Kurz, which targets a wide range of molecular changes that are involved in cancer development. In other words, this review is primarily driven by the findings from studies of Baicalein therapy in several cancer cell populations based on promising pre-clinical research. The modifications of numerous signal transduction mechanisms and transcriptional agents have been highlighted as the major players for Baicalein's anti-malignant properties at the micro level. These include AKT serine/threonine protein kinase B (AKT) as well as PI3K/Akt/mTOR, matrix metalloproteinases-2 & 9 (MMP-2 & 9), Wnt/-catenin, Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), NF-κB, Caspase-3/8/9, Smad4, Notch 1/Hes, Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1 (Keap 1), Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), Src/Id1, ROS signaling, miR 183/ezrin, and Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling cascades. The promise of Baicalein as an anti-inflammatory to anti-apoptotic/anti-angiogenic/anti-metastatic medicinal element for treating various malignancies and its capability to inhibit malignant stem cells, evidence of synergistic effects, and design of nanomedicine-based drugs are altogether well supported by the data presented in this review study.
Keywords: Baicalein; ROS; angiogenesis; anti-inflammatory; apoptosis; autophagy; flavonoids; nanomedicine; synergistic effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Baicalein: A metabolite with promising antineoplastic activity.Life Sci. 2020 Oct 15;259:118183. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118183. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32781058 Review.
-
Baicalein Ameliorates Insulin Resistance of HFD/STZ Mice Through Activating PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway of Liver and Skeletal Muscle in a GLP-1R-Dependent Manner.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 16;13(10):1246. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101246. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456499 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalein enhanced cisplatin sensitivity of gastric cancer cells by inducing cell apoptosis and autophagy via Akt/mTOR and Nrf2/Keap 1 pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Oct 20;531(3):320-327. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.07.045. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32800561
-
The Fascinating Effects of Baicalein on Cancer: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 9;17(10):1681. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101681. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27735841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baicalein protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity through activation of Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 and involving PKCα and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways.J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Aug 22;60(33):8171-82. doi: 10.1021/jf301511m. Epub 2012 Aug 9. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22838648
Cited by
-
Exploring baicalein: A natural flavonoid for enhancing cancer prevention and treatment.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 28;10(23):e40809. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40809. eCollection 2024 Dec 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39691196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating gastric cancer mechanisms and therapeutic potential of Adociaquinone A targeting EGFR: A genomic analysis and Computer Aided Drug Design (CADD) approach.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Oct;28(20):e70133. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70133. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39434198 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antiviral Activity, and Mechanisms of Action of Plant Polyphenols.Microorganisms. 2024 Dec 4;12(12):2502. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122502. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39770706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An updated review summarizing the anticancer potential of flavonoids via targeting NF-kB pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 6;15:1513422. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1513422. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39834817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of natural compounds in targeting cancer stem cells: a promising approach for cancer treatment.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 28;16(1):1433. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03190-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40721907 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Crans D.C., Yang L., Haase A., Yang X. Health benefits of vanadium and its potential as an anticancer agent. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2018;18:251–279. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

