Lipid Metabolic Reprogramming in Embryonal Neoplasms with MYCN Amplification
- PMID: 37046804
- PMCID: PMC10093342
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15072144
Lipid Metabolic Reprogramming in Embryonal Neoplasms with MYCN Amplification
Abstract
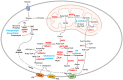
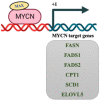
Tumor cells reprogram their metabolism, including glucose, glutamine, nucleotide, lipid, and amino acids to meet their enhanced energy demands, redox balance, and requirement of biosynthetic substrates for uncontrolled cell proliferation. Altered lipid metabolism in cancer provides lipids for rapid membrane biogenesis, generates the energy required for unrestricted cell proliferation, and some of the lipids act as signaling pathway mediators. In this review, we focus on the role of lipid metabolism in embryonal neoplasms with MYCN dysregulation. We specifically review lipid metabolic reactions in neuroblastoma, retinoblastoma, medulloblastoma, Wilms tumor, and rhabdomyosarcoma and the possibility of targeting lipid metabolism. Additionally, the regulation of lipid metabolism by the MYCN oncogene is discussed.
Keywords: MYCN; cancer; embryonal tumors; lipid metabolism; therapeutic targeting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Klempnauer K.H., Varmus H.E., Bishop J.M., Gilbert F., Brodeur G., Goldstein M., Trent J. Amplified DNA with Limited Homology to Myc Cellular Oncogene Is Shared by Human Neuroblastoma Cell Lines and a Neuroblastoma Tumour. Nature. 1983;305:245–248. doi: 10.1038/305245a0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

