Complementary and Alternative Medicines in Northern Cyprus: Public Awareness, Patterns of Use, and Attitudes
- PMID: 37046904
- PMCID: PMC10094393
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11070977
Complementary and Alternative Medicines in Northern Cyprus: Public Awareness, Patterns of Use, and Attitudes
Abstract
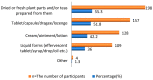
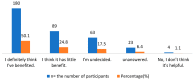
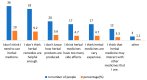
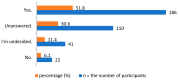
Background: The utilization of herbal medicine (HM) as a component of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is increasing worldwide. Little is known about justifications for its use and the factors associated with it. This study gains insights into the use of herbal medicines in Northern Cyprus, concentrating on targets for its use, the role played by disease type, reasons for its use, and sources of information. Methods: A questionnaire was utilized to achieve the aim of the study. The questionnaire was distributed to a random sample comprised of people in two different regions in Northern Cyprus over a 12-week period from August to November 2020. A self-administered questionnaire was used for data collection. Moreover, qualitative research explored individuals' decision making regarding CAM, which aimed to examine 20 patients as a context for beliefs, decision making, and dialogue about CAM. After audio-taping and verbatim transcription, the data were analyzed with qualitative content analysis. Results: The findings show that the majority of respondents learned about herbal products (HPs) and CAM from other patients, the Internet, friends, and family. The results indicate that almost half of the respondents were aware of how CAMs, especially herbal preparations, are used to treat common illnesses. Fennel, ginger, and echinacea were the most commonly used HMs, mainly for the treatment of the common cold. Furthermore, nearly 50% of the participants expressed the belief that HMs are safe, have fewer side effects than conventional medicines, and are also effective for treating minor health conditions. The prevalence was strongly associated with education level based on a Pearson Chi-square analysis. Conclusions: Although herbal medicines were mostly used to treat mild to moderate ailments and the participants were aware of their limitations, the combination of self-medication, inexperienced counseling, and lack of awareness of the risks of herbal medicines is potentially harmful. This is particularly important for elderly users, because although they seemed to be more aware of health-related issues, they generally used more medication than younger people. Given our finding that dissatisfaction with modern medicine is the most important reason for the preferred use of herbal medicines, government agencies, physicians, and pharmaceutical companies should be aware of this issue and should aim to create some level of awareness among users.
Keywords: Northern Cyprus; common illnesses; complementary and alternative medicine; herbal medicine; herbal products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Why people use herbal medicine: insights from a focus-group study in Germany.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Mar 15;18(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2160-6. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29544493 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence and determinants of complementary medicine use for nigerian children in the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus.Niger J Clin Pract. 2020 Aug;23(8):1054-1060. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_577_19. Niger J Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32788481
-
Habits, Traditions, and Beliefs Associated With the Use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine Among Diabetic Patients in Al-Qassim Region, Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2022 Dec 31;14(12):e33157. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33157. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36726934 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer patients taking herbal medicines: A review of clinical purposes, associated factors, and perceptions of benefit or harm.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 4;175:58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.052. Epub 2015 Sep 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26344852 Review.
-
The use of botanicals during pregnancy and lactation.Altern Ther Health Med. 2009 Jan-Feb;15(1):54-8. Altern Ther Health Med. 2009. PMID: 19161049 Review.
Cited by
-
Varieties of silence - a mixed-methods study exploring reasons and justifications for nondisclosure of the use of complementary therapies to physicians in Finland.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Sep 19;24(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04640-w. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 39300393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Larsen H.R. Alternative medicine: Why so popular. Int. Health News. 1999;93
-
- Millstine D. Types of complementary and alternative medicine. Merck Man. [(accessed on 24 March 2023)]. Available online: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/types-of-....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

