Epothilones as Natural Compounds for Novel Anticancer Drugs Development
- PMID: 37047035
- PMCID: PMC10093981
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076063
Epothilones as Natural Compounds for Novel Anticancer Drugs Development
Abstract
Epothilone is a natural 16-membered macrolide cytotoxic compound produced by the metabolism of the cellulose-degrading myxobacterium Sorangium cellulosum. This review summarizes results in the study of epothilones against cancer with preclinical results and clinical studies from 2010-2022. Epothilone have mechanisms of action similar to paclitaxel by inducing tubulin polymerization and apoptosis with low susceptibility to tumor resistance mechanisms. It is active against refractory tumors, being superior to paclitaxel in many respects. Since the discovery of epothilones, several derivatives have been synthesized, and most of them have failed in Phases II and III in clinical trials; however, ixabepilone and utidelone are currently used in clinical practice. There is robust evidence that triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) treatment improves using ixabepilone plus capecitabine or utidelone in combination with capecitabine. In recent years innovative synthetic strategies resulted in the synthesis of new epothilone derivatives with improved activity against refractory tumors with better activities when compared to ixabepilone or taxol. These compounds together with specific delivery mechanisms could be developed in anti-cancer drugs.
Keywords: anticancer agents; clinical trials; cytotoxicity; epothilone derivates; epothilones; refractory cancer; taxanes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

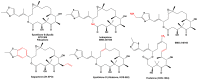
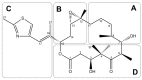

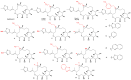
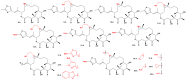
References
-
- Höfle G.R.H. Epothilone, a Myxobacterial Metabolite with Promising Antitumor Activity. In: Cragg G.M.K.D., Newman D.J., editors. Anticancer Agents from Natural Products. 1st ed. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2005. pp. 413–450.
-
- Höfle G., Bedorf N., Steinmetz H., Schomburg D., Gerth K., Reichenbach H. Epothilone A and B—Novel 16-Membered Macrolides with Cytotoxic Activity: Isolation, Crystal Structure, and Conformation in Solution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1996;35:1567–1569. doi: 10.1002/anie.199615671. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

