The Small RNA Landscape in NSCLC: Current Therapeutic Applications and Progresses
- PMID: 37047090
- PMCID: PMC10093969
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076121
The Small RNA Landscape in NSCLC: Current Therapeutic Applications and Progresses
Abstract
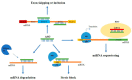
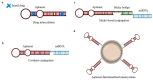
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the second most diagnosed type of malignancy and the first cause of cancer death worldwide. Despite recent advances, the treatment of choice for NSCLC patients remains to be chemotherapy, often showing very limited effectiveness with the frequent occurrence of drug-resistant phenotype and the lack of selectivity for tumor cells. Therefore, new effective and targeted therapeutics are needed. In this context, short RNA-based therapeutics, including Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs), microRNAs (miRNAs), short interfering (siRNA) and aptamers, represent a promising class of molecules. ASOs, miRNAs and siRNAs act by targeting and inhibiting specific mRNAs, thus showing an improved specificity compared to traditional anti-cancer drugs. Nucleic acid aptamers target and inhibit specific cancer-associated proteins, such as "nucleic acid antibodies". Aptamers are also able of receptor-mediated cell internalization, and therefore, they can be used as carriers of secondary agents giving the possibility of producing very highly specific and effective therapeutics. This review provides an overview of the proposed applications of small RNAs for NSCLC treatment, highlighting their advantageous features and recent advancements in the field.
Keywords: ASO; NSCLC; RNAi; aptamer; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Non-Viral RNA Therapies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Their Corresponding Clinical Trials.Mol Pharm. 2025 Apr 7;22(4):1752-1774. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.4c00871. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Mol Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40131145 Review.
-
Antitumoral RNA-targeted oligonucleotide therapeutics: The third pillar after small molecule inhibitors and antibodies.Cancer Sci. 2022 Sep;113(9):2952-2961. doi: 10.1111/cas.15461. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 35701833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Oligonucleotide Aptamers for NSCLC Targeting.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 23;21(17):6075. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176075. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32842557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current progress on aptamer-targeted oligonucleotide therapeutics.Ther Deliv. 2013 Dec;4(12):1527-46. doi: 10.4155/tde.13.118. Ther Deliv. 2013. PMID: 24304250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleic Acid Therapeutics in Huntington's Disease.Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2019;13(3):187-206. doi: 10.2174/1872208313666190208163714. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30747088 Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamers' Potential to Fill Therapeutic and Diagnostic Gaps.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 12;17(1):105. doi: 10.3390/ph17010105. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256938 Free PMC article.
-
Nature's carriers: leveraging extracellular vesicles for targeted drug delivery.Drug Deliv. 2024 Dec;31(1):2361165. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2024.2361165. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 38832506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive review of LncRNA-mediated therapeutic resistance in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Nov 9;24(1):369. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03549-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39522033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Nucleic Acid Research: Exploring the Potential of Oligonucleotides for Therapeutic Applications and Biological Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 21;25(1):146. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010146. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203317 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2022. American Cancer Society. 2022. [(accessed on 16 March 2023)]. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

