Faecal Microbiota Transplantation, Paving the Way to Treat Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- PMID: 37047094
- PMCID: PMC10094628
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076123
Faecal Microbiota Transplantation, Paving the Way to Treat Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is currently the most prevalent cause of chronic liver disease (CLD). Currently, the only therapeutic recommendation available is a lifestyle change. However, adherence to this approach is often difficult to guarantee. Alteration of the microbiota and an increase in intestinal permeability seem to be key in the development and progression of NAFLD. Therefore, the manipulation of microbiota seems to provide a promising therapeutic strategy. One way to do so is through faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). Here, we summarize the key aspects of FMT, detail its current indications and highlight the most recent advances in NAFLD.
Keywords: dysbiosis; faecal microbiota transplantation; gut microbiota; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
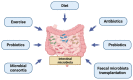
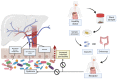
References
-
- Estes C., Anstee Q.M., Arias-Loste M.T., Bantel H., Bellentani S., Caballeria J., Colombo M., Craxi A., Crespo J., Day C.P., et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018;69:896–904. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.036. - DOI - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2016;64:1388–1402. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

