Photoprotective Effects of Dendrobium nobile Lindl. Polysaccharides against UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in HaCaT Cells
- PMID: 37047098
- PMCID: PMC10094248
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076120
Photoprotective Effects of Dendrobium nobile Lindl. Polysaccharides against UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in HaCaT Cells
Abstract
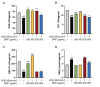
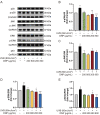
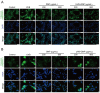
Acute ultraviolet (UV)-B radiation is the major external factor causing photodamage. In this study, we aimed to determine the effects of Dendrobium nobile Lindl. polysaccharides (DNPs) on photodamage in HaCaT keratinocytes after UVB irradiation and the underlying mechanisms. We found that DNPs significantly attenuated the decline in the viability and proliferation of HaCaT cells after UVB irradiation. Moreover, DNPs scavenged reactive oxygen species (ROS), improved the activities of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, and reduced the levels of malondialdehyde, while partially attenuating cell cycle arrest, suggesting their antioxidant and anti-apoptotic properties. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway was found to be important for the attenuation of UVB-induced photodamage in the HaCaT cells. Furthermore, DNPs exerted cytoprotective effects by downregulating UVB-induced ROS-mediated phosphorylation of MAPKs, including p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and by inhibiting p53 expression as well as the apoptotic cascade response. Therefore, DNPs ameliorated UVB-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in HaCaT cells via the regulation of MAPKs. Our findings thus highlight the Dendrobium nobile Lindl polysaccharides as promising therapeutic candidates for UVB-induced photodamage.
Keywords: Dendrobium nobile Lindl polysaccharides; HaCaT keratinocytes; MAPK; anti-apoptosis; antioxidant; ultraviolet B (UVB).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
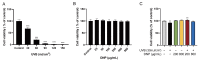






Similar articles
-
Dendrobium nobile Lindl. Polysaccharides protect fibroblasts against UVA-induced photoaging via JNK/c-Jun/MMPs pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;298:115590. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115590. Epub 2022 Aug 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35973631
-
Dendrobium nobile Lindl Polysaccharides Attenuate UVB-induced Photodamage by Regulating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and MMPs Expression in Mice Model.Photochem Photobiol. 2023 Sep-Oct;99(5):1269-1281. doi: 10.1111/php.13780. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Photochem Photobiol. 2023. PMID: 36651803
-
Allicin attenuates UVB-induced photodamage of keratinocytes by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes and activating the PI3K/Akt pathway.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Dec 14;317(1):124. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03599-5. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 39673634 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of the chemical composition of Dendrobium nobile Lindl.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 11;14:1163830. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1163830. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37497110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendrobium as a new natural source of bioactive for the prevention and treatment of digestive tract diseases: A comprehensive review with future perspectives.Phytomedicine. 2023 Jun;114:154784. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154784. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37011417 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in polysaccharides derived from the Dendrobium nobile Lindl.: preparation strategies, structural characteristics, biological activity, and structure-activity relationships.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1631637. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1631637. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40777987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The extract of buddleja officinalis maxim. alleviates UVB-induced oxidative damage via the NRF2 pathway in HaCaT cells.Pharm Biol. 2025 Dec;63(1):567-581. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2025.2540348. Epub 2025 Aug 7. Pharm Biol. 2025. PMID: 40771174 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on the regulatory and pharmacological mechanism of chemical components of Dendrobium.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 7;10(18):e37541. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37541. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39328574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vorinostat attenuates UVB-induced skin senescence by modulating NF-κB and mTOR signaling pathways.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 29;15(1):10905. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95624-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40158057 Free PMC article.
-
Dendrobium Nobile Polysaccharides Attenuates Ferroptosis and Improves Cognitive Function in Vascular Dementia Rats.Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2023 Jan-Dec;38:15333175231185236. doi: 10.1177/15333175231185236. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2023. PMID: 37342000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afnan Q., Kaiser P.J., Rafiq R.A., Nazir L.A., Bhushan S., Bhardwaj S.C., Sandhir R., Tasduq S.A. Glycyrrhizic acid prevents ultraviolet-B-induced photodamage: A role for mitogen-activated protein kinases, nuclear factor kappa B and mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Exp. Dermatol. 2016;25:440–446. doi: 10.1111/exd.12964. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

