Wds-Mediated H3K4me3 Modification Regulates Lipid Synthesis and Transport in Drosophila
- PMID: 37047100
- PMCID: PMC10093852
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076125
Wds-Mediated H3K4me3 Modification Regulates Lipid Synthesis and Transport in Drosophila
Abstract
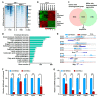
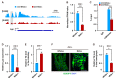
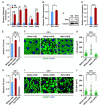
Lipid homeostasis is essential for insect growth and development. The complex of proteins associated with Set 1 (COMPASS)-catalyzed Histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) epigenetically activates gene transcription and is involved in various biological processes, but the role and molecular mechanism of H3K4me3 modification in lipid homeostasis remains largely unknown. In the present study, we showed in Drosophila that fat body-specific knockdown of will die slowly (Wds) as one of the COMPASS complex components caused a decrease in lipid droplet (LD) size and triglyceride (TG) levels. Mechanistically, Wds-mediated H3K4me3 modification in the fat body targeted several lipogenic genes involved in lipid synthesis and the Lpp gene associated with lipid transport to promote their expressions; the transcription factor heat shock factor (Hsf) could interact with Wds to modulate H3K4me3 modification within the promoters of these targets; and fat body-specific knockdown of Hsf phenocopied the effects of Wds knockdown on lipid homeostasis in the fat body. Moreover, fat body-specific knockdown of Wds or Hsf reduced high-fat diet (HFD)-induced oversized LDs and high TG levels. Altogether, our study reveals that Wds-mediated H3K4me3 modification is required for lipid homeostasis during Drosophila development and provides novel insights into the epigenetic regulation of insect lipid metabolism.
Keywords: H3K4me3; Hsf; Wds; fat body; intestine; lipid synthesis; lipid transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cardiomyocyte Regulation of Systemic Lipid Metabolism by the Apolipoprotein B-Containing Lipoproteins in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2017 Jan 17;13(1):e1006555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006555. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28095410 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H3K27 methylation-mediated repression of Hairy regulates insect developmental transition by modulating ecdysone biosynthesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Aug 31;118(35):e2101442118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2101442118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34429358 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor interaction with COMPASS-like complex regulates histone H3K4 trimethylation for specific gene expression in plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Mar 3;112(9):2900-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1419703112. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25730865 Free PMC article.
-
Broad domains of histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation in transcriptional regulation and disease.FEBS J. 2020 Jul;287(14):2891-2902. doi: 10.1111/febs.15219. Epub 2020 Feb 4. FEBS J. 2020. PMID: 31967712 Review.
-
H3K4me3 mediates uterine leiomyoma pathogenesis via neuronal processes, synapsis components, proliferation, and Wnt/β-catenin and TGF-β pathways.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2023 Jan 26;21(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12958-023-01060-2. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 36703136 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

