Metabiotics Signature through Genome Sequencing and In Vitro Inhibitory Assessment of a Novel Lactococcus lactis Strain UTNCys6-1 Isolated from Amazonian Camu-Camu Fruits
- PMID: 37047101
- PMCID: PMC10094308
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076127
Metabiotics Signature through Genome Sequencing and In Vitro Inhibitory Assessment of a Novel Lactococcus lactis Strain UTNCys6-1 Isolated from Amazonian Camu-Camu Fruits
Abstract
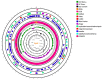
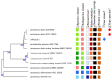
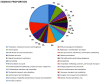
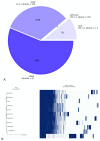
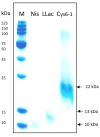
Metabiotics are the structural components of probiotic bacteria, functional metabolites, and/or signaling molecules with numerous beneficial properties. A novel Lactococcus lactis strain, UTNCys6-1, was isolated from wild Amazonian camu-camu fruits (Myrciaria dubia), and various functional metabolites with antibacterial capacity were found. The genome size is 2,226,248 base pairs, and it contains 2248 genes, 2191 protein-coding genes (CDSs), 50 tRNAs, 6 rRNAs, 1 16S rRNA, 1 23S rRNA, and 1 tmRNA. The average GC content is 34.88%. In total, 2148 proteins have been mapped to the EggNOG database. The specific annotation consisted of four incomplete prophage regions, one CRISPR-Cas array, six genomic islands (GIs), four insertion sequences (ISs), and four regions of interest (AOI regions) spanning three classes of bacteriocins (enterolysin_A, nisin_Z, and sactipeptides). Based on pangenome analysis, there were 6932 gene clusters, of which 751 (core genes) were commonly observed within the 11 lactococcal strains. Among them, 3883 were sample-specific genes (cloud genes) and 2298 were shell genes, indicating high genetic diversity. A sucrose transporter of the SemiSWEET family (PTS system: phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent transport system) was detected in the genome of UTNCys6-1 but not the other 11 lactococcal strains. In addition, the metabolic profile, antimicrobial susceptibility, and inhibitory activity of both protein-peptide extract (PPE) and exopolysaccharides (EPSs) against several foodborne pathogens were assessed in vitro. Furthermore, UTNCys6-1 was predicted to be a non-human pathogen that was unable to tolerate all tested antibiotics except gentamicin; metabolized several substrates; and lacks virulence factors (VFs), genes related to the production of biogenic amines, and acquired antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). Overall, this study highlighted the potential of this strain for producing bioactive metabolites (PPE and EPSs) for agri-food and pharmaceutical industry use.
Keywords: Lactococcus lactis; SemiSWEET sucrose transporter; antimicrobials; exopolysaccharides; metabiotics; pangenome.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Lactococcus-Specific Bacteriocins Produced by Lactococcal Isolates, and the Discovery of a Novel Bacteriocin, Lactococcin Z.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2015 Sep;7(3):222-31. doi: 10.1007/s12602-015-9196-4. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2015. PMID: 26093857
-
The ability of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis bv. diacetylactis strains in producing nisin.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2020 May;113(5):651-662. doi: 10.1007/s10482-019-01373-6. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2020. PMID: 31838601
-
Bioprospecting of Ribosomally Synthesized and Post-translationally Modified Peptides Through Genome Characterization of a Novel Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum UTNGt21A Strain: A Promising Natural Antimicrobials Factory.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 6;13:868025. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.868025. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35464932 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial production of bacteriocins: Latest research development and applications.Biotechnol Adv. 2018 Dec;36(8):2187-2200. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.10.007. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Biotechnol Adv. 2018. PMID: 30385277 Review.
-
[Antibacterial metabolites of lactic acid bacteria: their diversity and properties].Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol. 2012 May-Jun;48(3):259-75. Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol. 2012. PMID: 22834296 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Fruit and Vegetable Juices as Functional Carriers for Probiotic Delivery: Microbiological, Nutritional, and Sensory Perspectives.Microorganisms. 2025 May 30;13(6):1272. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061272. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virulence, Antibiotic Resistance and Cytotoxic Effects of Lactococcus lactis Isolated from Chinese Cows with Clinical Mastitis on MAC-T Cells.Microorganisms. 2025 Jul 16;13(7):1674. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13071674. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40732181 Free PMC article.
-
Frequently asked questions about the ISAPP postbiotic definition.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 10;14:1324565. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1324565. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38268705 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

