The Liver and Glycogen: In Sickness and in Health
- PMID: 37047105
- PMCID: PMC10094386
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076133
The Liver and Glycogen: In Sickness and in Health
Abstract
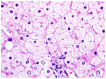
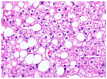
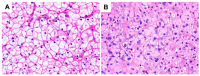
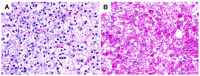
The liver is a major store of glycogen and is essential in maintaining systemic glucose homeostasis. In healthy individuals, glycogen synthesis and breakdown in the liver are tightly regulated. Abnormal glycogen metabolism results in prominent pathological changes in the liver, often manifesting as hepatic glycogenosis or glycogen inclusions. This can occur in genetic glycogen storage disease or acquired conditions with insulin dysregulation such as diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or medication effects. Some primary hepatic tumors such as clear cell hepatocellular carcinoma also demonstrate excessive glycogen accumulation. This review provides an overview of the pathological manifestations and molecular mechanisms of liver diseases associated with abnormal glycogen accumulation.
Keywords: Mauriac syndrome; clear cell hepatocellular carcinoma; glycogenic hepatopathy; hepatic glycogenosis; pathology; pseudoground glass.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

