Interplay of Vitamin D and SIRT1 in Tissue-Specific Metabolism-Potential Roles in Prevention and Treatment of Non-Communicable Diseases Including Cancer
- PMID: 37047134
- PMCID: PMC10094444
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076154
Interplay of Vitamin D and SIRT1 in Tissue-Specific Metabolism-Potential Roles in Prevention and Treatment of Non-Communicable Diseases Including Cancer
Abstract
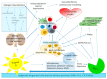
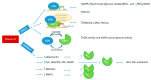
The importance of the prevention and control of non-communicable diseases, including obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer, is increasing as a requirement of the aging population in developed countries and the sustainability of healthcare. Similarly, the 2013-2030 action plan of the WHO for the prevention and control of non-communicable diseases seeks these achievements. Adequate lifestyle changes, alone or with the necessary treatments, could reduce the risk of mortality or the deterioration of quality of life. In our recent work, we summarized the role of two central factors, i.e., appropriate levels of vitamin D and SIRT1, which are connected to adequate lifestyles with beneficial effects on the prevention and control of non-communicable diseases. Both of these factors have received increased attention in relation to the COVID-19 pandemic as they both take part in regulation of the main metabolic processes, i.e., lipid/glucose/energy homeostasis, oxidative stress, redox balance, and cell fate, as well as in the healthy regulation of the immune system. Vitamin D and SIRT1 have direct and indirect influence of the regulation of transcription and epigenetic changes and are related to cytoplasmic signaling pathways such as PLC/DAG/IP3/PKC/MAPK, MEK/Erk, insulin/mTOR/cell growth, proliferation; leptin/PI3K-Akt-mTORC1, Akt/NFĸB/COX-2, NFĸB/TNFα, IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and AMPK/PGC-1α/GLUT4, among others. Through their proper regulation, they maintain normal body weight, lipid profile, insulin secretion and sensitivity, balance between the pro- and anti-inflammatory processes under normal conditions and infections, maintain endothelial health; balance cell differentiation, proliferation, and fate; and balance the circadian rhythm of the cellular metabolism. The role of these two molecules is interconnected in the molecular network, and they regulate each other in several layers of the homeostasis of energy and the cellular metabolism. Both have a central role in the maintenance of healthy and balanced immune regulation and redox reactions; therefore, they could constitute promising targets either for prevention or as complementary therapies to achieve a better quality of life, at any age, for healthy people and patients under chronic conditions.
Keywords: SIRT1; epigenetics; metabolism; prevention and treatment; signaling pathways; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
The Role of Epigenetic Regulator SIRT1 in Balancing the Homeostasis and Preventing the Formation of Specific "Soil" of Metabolic Disorders and Related Cancers.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):253. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709253. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224002 Review.
-
The Role of Vitamin D and Its Molecular Bases in Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome, and Cardiovascular Disease: State of the Art.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 23;24(20):15485. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015485. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D supplementation inhibits oxidative stress and upregulate SIRT1/AMPK/GLUT4 cascade in high glucose-treated 3T3L1 adipocytes and in adipose tissue of high fat diet-fed diabetic mice.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Feb 1;615:22-34. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28063949
-
Essential sufficiency of zinc, ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamin D and magnesium for prevention and treatment of COVID-19, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, lung diseases and cancer.Biochimie. 2021 Aug;187:94-109. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2021.05.013. Epub 2021 May 31. Biochimie. 2021. PMID: 34082041 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D status with cardiometabolic risk factors and total and regional obesity in southern Iran: evidence from the PoCOsteo study.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 3;14(1):17983. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68773-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39097599 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and Colorectal Cancer Prevention: Immunological Mechanisms, Inflammatory Pathways, and Nutritional Implications.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 15;17(8):1351. doi: 10.3390/nu17081351. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40284214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From the Sun to the Cell: Examining Obesity through the Lens of Vitamin D and Inflammation.Metabolites. 2023 Dec 20;14(1):4. doi: 10.3390/metabo14010004. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 38276294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Aspects in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes and Possible Preventive and Complementary Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 22;25(16):9113. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169113. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin 1 mediates the pro-survival effects of vitamin D in angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy of H9c2 cardiomyoblasts.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Dec 31;52(1):96. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10168-6. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738677
References
-
- Martins I.J. COVID-19 Infection and Anti-Aging Gene Inactivation. Acta Sci. Nutr. Health. 2020;4:29554–29573. doi: 10.31080/ASNH.2020.04.0690. - DOI
-
- Li A., Shen P., Liu S., Wang J., Zeng J., Du C. Vitamin D alleviates skeletal muscle loss and insulin resistance by inducing vitamin D receptor expression and regulating the AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway in mice. Food Sci. Technol. 2022;42:e47921. doi: 10.1590/fst.47921. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

