The Attenuation of Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling Pathway Plays a Crucial Role in the Myo-Inositol-Alleviated Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 37047164
- PMCID: PMC10094297
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076194
The Attenuation of Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling Pathway Plays a Crucial Role in the Myo-Inositol-Alleviated Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
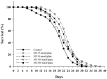
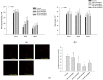
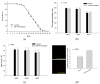
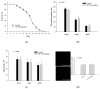
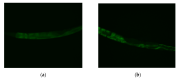
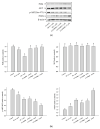
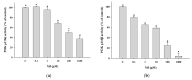
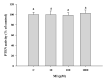
Myo-Inositol (MI) has been shown to alleviate aging in Caenorhabditis (C). elegans. However, the mechanism by which MI alleviates aging remains unclear. In this study, we investigate whether MI can modulate the PI3K so as to attenuate the insulin/IGF-1 signaling (IIS) pathway and exert the longevity effect. The wild-type C. elegans and two mutants of AKT-1 and DAF-16 were used to explore the mechanism of MI so as to extend the lifespan, as well as to improve the health indexes of pharyngeal pumping and body bend, and an aging marker of autofluorescence in the C. elegans. We confirmed that MI could significantly extend the lifespan of C. elegans. MI also ameliorated the pharyngeal pumping and body bend and decreased autofluorescence. We further adopted the approach to reveal the loss-of-function mutants to find the signaling mechanism of MI. The functions of the lifespan-extending, health-improving, and autofluorescence-decreasing effects of MI disappeared in the AKT-1 and DAF-16 mutants. MI could also induce the nuclear localization of the DAF-16. Importantly, we found that MI could dramatically inhibit the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) activity in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 90.2 μM for the p110α isoform of the PI3K and 21.7 μM for the p110β. In addition, the downregulation of the PI3K expression and the inhibition of the AKT phosphorylation by MI was also obtained. All these results demonstrate that MI can inhibit the PI3K activity and downregulate the PI3K expression, and the attenuation of the IIS pathway plays a crucial role for MI in alleviating aging in C. elegans.
Keywords: C. elegans; PI3K inhibitor; insulin/insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling pathway; longevity; myo-inositol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

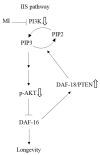
 as: “The inhibition step of MI or the inactivation step in the signaling pathway”, the symbol ⇩ as “The detected downregulation of protein expressions or protein phosphorylation by MI”, and ⇧ as “The detected upregulation of protein expression by MI” in this study. NB: the references are indicated in square brackets.
as: “The inhibition step of MI or the inactivation step in the signaling pathway”, the symbol ⇩ as “The detected downregulation of protein expressions or protein phosphorylation by MI”, and ⇧ as “The detected upregulation of protein expression by MI” in this study. NB: the references are indicated in square brackets.Similar articles
-
Regulation of the Caenorhabditis elegans longevity protein DAF-16 by insulin/IGF-1 and germline signaling.Nat Genet. 2001 Jun;28(2):139-45. doi: 10.1038/88850. Nat Genet. 2001. PMID: 11381260
-
Bisphenol S decreased lifespan and healthspan via insulin/IGF-1-like signaling-against mitochondrial stress in Caenorhabditis elegans.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Oct 15;285:117136. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.117136. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 39353373
-
LET-60 RAS modulates effects of insulin/IGF-1 signaling on development and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans.Aging Cell. 2005 Oct;4(5):235-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2005.00166.x. Aging Cell. 2005. PMID: 16164423
-
Insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling in C. elegans.WormBook. 2013 Dec 26:1-43. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.164.1. WormBook. 2013. PMID: 24395814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DAF-16 target identification in C. elegans: past, present and future.Biogerontology. 2015 Apr;16(2):221-34. doi: 10.1007/s10522-014-9527-y. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Biogerontology. 2015. PMID: 25156270 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Insulin Resistance-Molecular Mechanisms, Therapeutic Targets, and Future Directions.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 13;26(6):2574. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062574. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141215 Free PMC article.
-
APPA Increases Lifespan and Stress Resistance via Lipid Metabolism and Insulin/IGF-1 Signal Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 5;24(18):13682. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813682. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37761985 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Geroprotective Potential of Nutraceuticals.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 24;16(17):2835. doi: 10.3390/nu16172835. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of mitochondria in aging, cell death, and tumor immunity.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 23;15:1520072. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1520072. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39763653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anionic Methacrylate Copolymer Microparticles for the Delivery of Myo-Inositol Produced by Spray-Drying: In Vitro and In Vivo Bioavailability.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 29;25(7):3852. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073852. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612662 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

