Discovery of SNP Molecular Markers and Candidate Genes Associated with Sacbrood Virus Resistance in Apis cerana cerana Larvae by Whole-Genome Resequencing
- PMID: 37047210
- PMCID: PMC10094193
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076238
Discovery of SNP Molecular Markers and Candidate Genes Associated with Sacbrood Virus Resistance in Apis cerana cerana Larvae by Whole-Genome Resequencing
Abstract
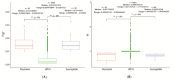
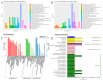
Sacbrood virus (SBV) is a significant problem that impedes brood development in both eastern and western honeybees. Whole-genome sequencing has become an important tool in researching population genetic variations. Numerous studies have been conducted using multiple techniques to suppress SBV infection in honeybees, but the genetic markers and molecular mechanisms underlying SBV resistance have not been identified. To explore single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), insertions, deletions (Indels), and genes at the DNA level related to SBV resistance, we conducted whole-genome resequencing on 90 Apis cerana cerana larvae raised in vitro and challenged with SBV. After filtering, a total of 337.47 gigabytes of clean data and 31,000,613 high-quality SNP loci were detected in three populations. We used ten databases to annotate 9359 predicted genes. By combining population differentiation index (FST) and nucleotide polymorphisms (π), we examined genome variants between resistant (R) and susceptible (S) larvae, focusing on site integrity (INT < 0.5) and minor allele frequency (MAF < 0.05). A selective sweep analysis with the top 1% and top 5% was used to identify significant regions. Two SNPs on the 15th chromosome with GenBank KZ288474.1_322717 (Guanine > Cytosine) and KZ288479.1_95621 (Cytosine > Thiamine) were found to be significantly associated with SBV resistance based on their associated allele frequencies after SNP validation. Each SNP was authenticated in 926 and 1022 samples, respectively. The enrichment and functional annotation pathways from significantly predicted genes to SBV resistance revealed immune response processes, signal transduction mechanisms, endocytosis, peroxisomes, phagosomes, and regulation of autophagy, which may be significant in SBV resistance. This study presents novel and useful SNP molecular markers that can be utilized as assisted molecular markers to select honeybees resistant to SBV for breeding and that can be used as a biocontrol technique to protect honeybees from SBV.
Keywords: Apis cerana cerana; larva; nucleotide polymorphisms; population differentiation index; sacbrood virus; sequencing; single nucleotide polymorphism; variants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Phylogeny and Pathogenesis of Sacbrood Virus (SBV) Infection in European Honey Bees, Apis mellifera.Viruses. 2019 Jan 14;11(1):61. doi: 10.3390/v11010061. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30646581 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of Apis cerana Sacbrood virus Infection in Apis mellifera.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Apr 4;82(8):2256-62. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03292-15. Print 2016 Apr. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26801569 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals various host responses to sacbrood virus infection in Apis cerana and Apis mellifera.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 1;26(1):592. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11779-4. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40597634 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic analysis and survey of Apis cerana strain of Sacbrood virus (AcSBV) in Taiwan suggests a recent introduction.J Invertebr Pathol. 2017 Jun;146:36-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 5. J Invertebr Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28390783
-
Sacbrood Virus: A Growing Threat to Honeybees and Wild Pollinators.Viruses. 2022 Aug 25;14(9):1871. doi: 10.3390/v14091871. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146677 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ellis J.D., Munn P.A. The Worldwide Health Status of Honey Bees. Bee World. 2005;86:88–101. doi: 10.1080/0005772X.2005.11417323. - DOI
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

