Integrating AI/ML Models for Patient Stratification Leveraging Omics Dataset and Clinical Biomarkers from COVID-19 Patients: A Promising Approach to Personalized Medicine
- PMID: 37047222
- PMCID: PMC10094615
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076250
Integrating AI/ML Models for Patient Stratification Leveraging Omics Dataset and Clinical Biomarkers from COVID-19 Patients: A Promising Approach to Personalized Medicine
Abstract
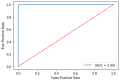
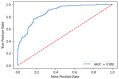
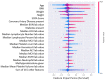
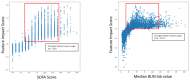
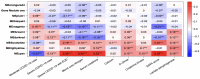
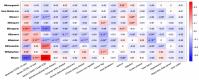
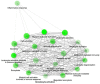
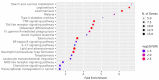
The COVID-19 pandemic has presented an unprecedented challenge to the healthcare system. Identifying the genomics and clinical biomarkers for effective patient stratification and management is critical to controlling the spread of the disease. Omics datasets provide a wealth of information that can aid in understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms of COVID-19 and identifying potential biomarkers for patient stratification. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms have been increasingly used to analyze large-scale omics and clinical datasets for patient stratification. In this manuscript, we demonstrate the recent advances and predictive accuracies in AI- and ML-based patient stratification modeling linking omics and clinical biomarker datasets, focusing on COVID-19 patients. Our ML model not only demonstrates that clinical features are enough of an indicator of COVID-19 severity and survival, but also infers what clinical features are more impactful, which makes our approach a useful guide for clinicians for prioritization best-fit therapeutics for a given cohort of patients. Moreover, with weighted gene network analysis, we are able to provide insights into gene networks that have a significant association with COVID-19 severity and clinical features. Finally, we have demonstrated the importance of clinical biomarkers in identifying high-risk patients and predicting disease progression.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; artificial intelligence; omics; patient stratification; risk management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are all employees of VeriSIM Life and used a proprietary AI/ML-driven platform to generate the outcomes for the manuscript.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Benchmarking of Machine Learning classifiers on plasma proteomic for COVID-19 severity prediction through interpretable artificial intelligence.Artif Intell Med. 2023 Mar;137:102490. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2023.102490. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Artif Intell Med. 2023. PMID: 36868685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomics, Microbiomics, Machine learning during the COVID-19 pandemic.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2022 Jan;33 Suppl 27(Suppl 27):86-88. doi: 10.1111/pai.13640. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35080309 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Identifying Vital Biomarkers with Greater Precision in Emergency Departments During Emerging Pandemics.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 16;26(2):722. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020722. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859435 Free PMC article.
-
Precision medicine in colorectal cancer: Leveraging multi-omics, spatial omics, and artificial intelligence.Clin Chim Acta. 2024 Jun 1;559:119686. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2024.119686. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Clin Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38663471 Review.
-
Predicting the Disease Severity of Virus Infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1368:111-139. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-8969-7_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35594023
Cited by
-
From Serendipity to Precision: Integrating AI, Multi-Omics, and Human-Specific Models for Personalized Neuropsychiatric Care.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 12;13(1):167. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010167. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutting-edge AI tools revolutionizing scientific research in life sciences.BioTechnologia (Pozn). 2025 Mar 31;106(1):77-102. doi: 10.5114/bta/200803. eCollection 2025. BioTechnologia (Pozn). 2025. PMID: 40401131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing Clinical Management of COVID-19: A Predictive Model for Unvaccinated Patients Admitted to ICU.Pathogens. 2025 Feb 27;14(3):230. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14030230. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40137715 Free PMC article.
-
Explainable artificial intelligence approaches for COVID-19 prognosis prediction using clinical markers.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 20;14(1):1783. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52428-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38245638 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing clinical biochemistry: addressing gaps and driving future innovations.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 8;12:1521126. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1521126. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40265187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee B., Lewis G., Agyei-Manu E., Atkins N., Bhattacharyya U., Dozier M., Rostron J., Sheikh A., McQuillan R., Theodoratou E., et al. Risk of serious COVID-19 outcomes among adults and children with moderate-to-severe asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022;31:220066. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0066-2022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

