LTR Retroelements and Bird Adaptation to Arid Environments
- PMID: 37047324
- PMCID: PMC10094322
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076332
LTR Retroelements and Bird Adaptation to Arid Environments
Abstract
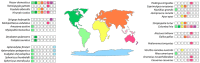
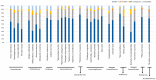
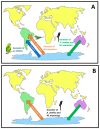
TEs are known to be among the main drivers in genome evolution, leading to the generation of evolutionary advantages that favor the success of organisms. The aim of this work was to investigate the TE landscape in bird genomes to look for a possible relationship between the amount of specific TE types and environmental changes that characterized the Oligocene era in Australia. Therefore, the mobilome of 29 bird species, belonging to a total of 11 orders, was analyzed. Our results confirmed that LINE retroelements are not predominant in all species of this evolutionary lineage and highlighted an LTR retroelement dominance in species with an Australian-related evolutionary history. The bird LTR retroelement expansion might have happened in response to the Earth's dramatic climate changes that occurred about 30 Mya, followed by a progressive aridification across most of Australian landmasses. Therefore, in birds, LTR retroelement burst might have represented an evolutionary advantage in the adaptation to arid/drought environments.
Keywords: Australian bird evolution; Aves; genome evolution; molecular adaptation; transposable elements; vertebrates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Canapa A., Biscotti M.A., Barucca M., Carducci F., Carotti E., Olmo E. Shedding light upon the complex net of genome size, genome composition and environment in chordates. Eur. Zool. J. 2020;87:192–202. doi: 10.1080/24750263.2020.1747558. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

