Main Pathogenic Mechanisms and Recent Advances in COPD Peripheral Skeletal Muscle Wasting
- PMID: 37047427
- PMCID: PMC10095391
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076454
Main Pathogenic Mechanisms and Recent Advances in COPD Peripheral Skeletal Muscle Wasting
Abstract
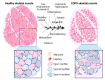
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a worldwide prevalent respiratory disease mainly caused by tobacco smoke exposure. COPD is now considered as a systemic disease with several comorbidities. Among them, skeletal muscle dysfunction affects around 20% of COPD patients and is associated with higher morbidity and mortality. Although the histological alterations are well characterized, including myofiber atrophy, a decreased proportion of slow-twitch myofibers, and a decreased capillarization and oxidative phosphorylation capacity, the molecular basis for muscle atrophy is complex and remains partly unknown. Major difficulties lie in patient heterogeneity, accessing patients' samples, and complex multifactorial process including extrinsic mechanisms, such as tobacco smoke or disuse, and intrinsic mechanisms, such as oxidative stress, hypoxia, or systemic inflammation. Muscle wasting is also a highly dynamic process whose investigation is hampered by the differential protein regulation according to the stage of atrophy. In this review, we report and discuss recent data regarding the molecular alterations in COPD leading to impaired muscle mass, including inflammation, hypoxia and hypercapnia, mitochondrial dysfunction, diverse metabolic changes such as oxidative and nitrosative stress and genetic and epigenetic modifications, all leading to an impaired anabolic/catabolic balance in the myocyte. We recapitulate data concerning skeletal muscle dysfunction obtained in the different rodent models of COPD. Finally, we propose several pathways that should be investigated in COPD skeletal muscle dysfunction in the future.
Keywords: cachexia; interleukin; metabolism; myocyte.
Conflict of interest statement
I.D. and P.B. have two patents delivered (EP no. 3050574, i.e., “Use of plerixafor for treating and/or preventing acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease”, EP no. 20173595.8, i.e., “New compositions and methods of treating COVID-19 disease”). PB is the medical coordinator of the French national cohort (i.e., COBRA), which received grants from AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKine, Roche, Chiesi, Novartis and Legs Poix foundation. Moreover, PB reports grants and personal fees from Novartis, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Chiesi, grants, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees and nonfinancial support from AstraZeneca, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Sanofi, personal fees from Menarini, personal fees from TEVA, outside the submitted work. All the other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 310 Diseases and Injuries, 1990–2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1545–1602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

