Thalidomide Attenuates Epileptogenesis and Seizures by Decreasing Brain Inflammation in Lithium Pilocarpine Rat Model
- PMID: 37047461
- PMCID: PMC10094940
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076488
Thalidomide Attenuates Epileptogenesis and Seizures by Decreasing Brain Inflammation in Lithium Pilocarpine Rat Model
Abstract
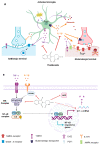
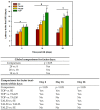
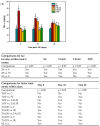
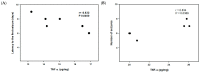
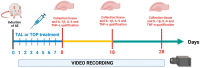
Thalidomide (TAL) has shown potential therapeutic effects in neurological diseases like epilepsy. Both clinical and preclinical studies show that TAL may act as an antiepileptic drug and as a possible treatment against disease development. However, the evidence for these effects is limited. Therefore, the antiepileptogenic and anti-inflammatory effects of TAL were evaluated herein. Sprague Dawley male rats were randomly allocated to one of five groups (n = 18 per group): control (C); status epilepticus (SE); SE-TAL (25 mg/kg); SE-TAL (50 mg/kg); and SE-topiramate (TOP; 60mg/kg). The lithium-pilocarpine model was used, and one day after SE induction the rats received pharmacological treatment for one week. The brain was obtained, and the hippocampus was micro-dissected 8, 18, and 28 days after SE. TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β concentrations were quantified. TOP and TAL (50 mg/kg) increased the latency to the first of many spontaneous recurrent seizures (SRS) and decreased SRS frequency, as well as decreasing TNF-α and IL-1β concentrations in the hippocampus. In conclusion, the results showed that both TAL (50 mg/kg) and TOP have anti-ictogenic and antiepileptogenic effects, possibly by decreasing neuroinflammation.
Keywords: anti-ictogenic; antiepileptogenic; neuroinflammation; temporal lobe epilepsy; thalidomide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The combination of topiramate and diazepam is partially neuroprotective in the hippocampus but not antiepileptogenic in the lithium-pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy.Epilepsy Res. 2006 Dec;72(2-3):147-63. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2006.07.014. Epub 2006 Sep 1. Epilepsy Res. 2006. PMID: 16945504
-
Anti-inflammatory treatment with a soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor attenuates seizures and epilepsy-associated depression in the LiCl-pilocarpine post-status epilepticus rat model.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Oct;81:535-544. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.07.014. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 31306773 Free PMC article.
-
Minocycline inhibits brain inflammation and attenuates spontaneous recurrent seizures following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus.Neuroscience. 2015 Feb 26;287:144-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.12.021. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25541249
-
Fingolimod (FTY720) inhibits neuroinflammation and attenuates spontaneous convulsions in lithium-pilocarpine induced status epilepticus in rat model.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012 Dec;103(2):187-96. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2012.08.025. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012. PMID: 22960129
-
Animal models of epilepsy for the development of antiepileptogenic and disease-modifying drugs. A comparison of the pharmacology of kindling and post-status epilepticus models of temporal lobe epilepsy.Epilepsy Res. 2002 Jun;50(1-2):105-23. doi: 10.1016/s0920-1211(02)00073-6. Epilepsy Res. 2002. PMID: 12151122 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on the role of inflammatory mediators in the pathogenesis of epilepsy.Ibrain. 2024 May 29;11(1):44-58. doi: 10.1002/ibra.12162. eCollection 2025 Spring. Ibrain. 2024. PMID: 40103702 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

