SMTP-44D Inhibits Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation in Apolipoprotein-E Null Mice Partly by Suppressing the AGEs-RAGE Axis
- PMID: 37047475
- PMCID: PMC10094964
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076505
SMTP-44D Inhibits Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation in Apolipoprotein-E Null Mice Partly by Suppressing the AGEs-RAGE Axis
Abstract
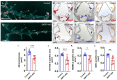
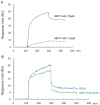
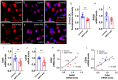
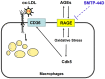
SMTP-44D has been reported to have anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory reactions, including reduced expression of receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Although activation of RAGE with its ligands, and advanced glycation end products (AGEs), play a crucial role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, a leading cause of death in diabetic patients, it remains unclear whether SMTP-44D could inhibit experimental atherosclerosis by suppressing the AGEs-RAGE axis. In this study, we investigated the effects of SMTP-44D on atherosclerotic plaque formation and expression of AGEs in apolipoprotein-E null (Apoe-/-) mice. We further studied here whether and how SMTP-44D inhibited foam cell formation of macrophages isolated from Apoe-/- mice ex vivo. Although administration of SMTP-44D to Apoe-/- mice did not affect clinical or biochemical parameters, it significantly decreased the surface area of atherosclerotic lesions and reduced the atheromatous plaque size, macrophage infiltration, and AGEs accumulation in the aortic roots. SMTP-44D bound to immobilized RAGE and subsequently attenuated the interaction of AGEs with RAGE in vitro. Furthermore, foam cell formation evaluated by Dil-oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) uptake, and gene expression of RAGE, cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) and CD36 in macrophages isolated from SMTP-44D-treated Apoe-/- mice were significantly decreased compared with those from saline-treated mice. Gene expression levels of RAGE and Cdk5 were highly correlated with each other, the latter of which was also positively associated with that of CD36. The present study suggests that SMTP-44D may inhibit atherosclerotic plaque formation in Apoe-/- mice partly by blocking the AGEs-RAGE-induced ox-LDL uptake into macrophages via the suppression of Cdk5-CD36 pathway.
Keywords: AGEs; CD36; Cdk5; RAGE; SMTP-44D; atherosclerosis; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
K.H. is director of the board of TMS Co., Ltd., TMS Co., Ltd. shareholder, and received grants from TMS Co., Ltd. and EPS Corporation, as well as license fees for SMTP-related patents. Y.M. holds an endowed chair funded by Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AGE-RAGE Axis Stimulates Oxidized LDL Uptake into Macrophages through Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 5-CD36 Pathway via Oxidative Stress Generation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 4;21(23):9263. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239263. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33291667 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of SMTP-44D in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathy mouse model.J Diabetes Complications. 2025 Jul;39(7):109061. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2025.109061. Epub 2025 Apr 29. J Diabetes Complications. 2025. PMID: 40318460
-
SMTP-44D alleviates diabetic retinopathy by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress in in vivo and in vitro models.J Pharmacol Sci. 2025 Feb;157(2):57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2024.12.004. Epub 2024 Dec 15. J Pharmacol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39828394
-
Advanced Glycation End Products: key player of the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.Glycoconj J. 2022 Aug;39(4):547-563. doi: 10.1007/s10719-022-10063-x. Epub 2022 May 17. Glycoconj J. 2022. PMID: 35579827 Review.
-
99mTc-Labeled anti-receptor for advanced glycation endproducts monoclonal antibody F(ab’)2 fragments.2010 Jul 16 [updated 2010 Aug 16]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2010 Jul 16 [updated 2010 Aug 16]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20734503 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
KLF7 reverses ox-LDL-induced ferroptosis in HMEC-1 cells through transcriptionally activating ALKBH5 to inhibit the m6A modification of ACSL4.Cytotechnology. 2024 Dec;76(6):653-666. doi: 10.1007/s10616-024-00641-2. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Cytotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39435423
-
Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Inhibits AGE-Induced NADPH Oxidase-Derived Oxidative Stress Generation and Foam Cell Formation in Macrophages Partly via AMPK Activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 8;25(17):9724. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179724. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Razaei M., Rabizadeh S., Mirahmad M., Hajmiri M.S., Nakhjavani M., Hemmatabadi M., Shirzad N. The association between advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and ABC (hemoglobin A1C, blood pressure, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) control parameters among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022;14:122. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00895-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kilhovd B.K., Juutilainen A., Lehto S., Rönnemaa T., Torjesen P.A., Hanssen K.F., Laakso M. Increased serum levels of advanced glycation endproducts predict total, cardiovascular and coronary mortality in women with type 2 diabetes: A population-based 18 year follow-up study. Diabetologia. 2007;50:1409–1417. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0687-z. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

