Ablation of Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Changes the Transcriptomic Profile and Alters Neural-Related Pathways in the Brain
- PMID: 37047515
- PMCID: PMC10095516
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076542
Ablation of Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Changes the Transcriptomic Profile and Alters Neural-Related Pathways in the Brain
Abstract
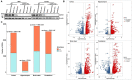
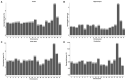
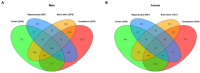
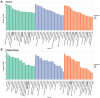
Death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1), a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent serine/threonine kinase, mediates various neuronal functions, including cell death. Abnormal upregulation of DAPK1 is observed in human patients with neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) and epilepsy. Ablation of DAPK1 expression and suppression of DAPK1 activity attenuates neuropathology and behavior impairments. However, whether DAPK1 regulates gene expression in the brain, and whether its gene profile is implicated in neuronal disorders, remains elusive. To reveal the function and pathogenic role of DAPK1 in neurological diseases in the brain, differential transcriptional profiling was performed in the brains of DAPK1 knockout (DAPK1-KO) mice compared with those of wild-type (WT) mice by RNA sequencing. We showed significantly altered genes in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, brain stem, and cerebellum of both male and female DAPK1-KO mice compared to those in WT mice, respectively. The genes are implicated in multiple neural-related pathways, including: AD, Parkinson's disease (PD), Huntington's disease (HD), neurodegeneration, glutamatergic synapse, and GABAergic synapse pathways. Moreover, our findings imply that the potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 1 (Kcna1) may be involved in the modulation of DAPK1 in epilepsy. Our study provides insight into the pathological role of DAPK1 in the regulatory networks in the brain and new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of neurological diseases.
Keywords: brain; death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1); differential transcriptional profiling; neurodegeneration; neuronal functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
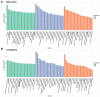


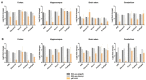
References
-
- Yamamoto M., Takahashi H., Nakamura T., Hioki T., Nagayama S., Ooashi N., Sun X., Ishii T., Kudo Y., Nakajima-Iijima S., et al. Developmental changes in distribution of death-associated protein kinase mRNAs. J. Neurosci. Res. 1999;58:674–683. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19991201)58:5<674::AID-JNR8>3.0.CO;2-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

