Delineation of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase Phosphorylation Sites within the D1 Dopamine Receptor and Their Roles in Modulating β-Arrestin Binding and Activation
- PMID: 37047571
- PMCID: PMC10095280
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076599
Delineation of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase Phosphorylation Sites within the D1 Dopamine Receptor and Their Roles in Modulating β-Arrestin Binding and Activation
Abstract
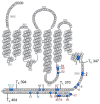
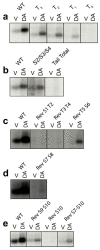
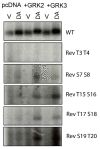
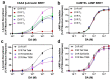
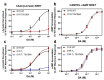
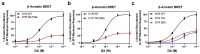
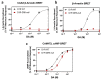
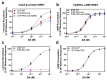
The D1 dopamine receptor (D1R) is a G protein-coupled receptor that signals through activating adenylyl cyclase and raising intracellular cAMP levels. When activated, the D1R also recruits the scaffolding protein β-arrestin, which promotes receptor desensitization and internalization, as well as additional downstream signaling pathways. These processes are triggered through receptor phosphorylation by G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs), although the precise phosphorylation sites and their role in recruiting β-arrestin to the D1R remains incompletely described. In this study, we have used detailed mutational and in situ phosphorylation analyses to completely identify the GRK-mediated phosphorylation sites on the D1R. Our results indicate that GRKs can phosphorylate 14 serine and threonine residues within the C-terminus and the third intracellular loop (ICL3) of the receptor, and that this occurs in a hierarchical fashion, where phosphorylation of the C-terminus precedes that of the ICL3. Using β-arrestin recruitment assays, we identified a cluster of phosphorylation sites in the proximal region of the C-terminus that drive β-arrestin binding to the D1R. We further provide evidence that phosphorylation sites in the ICL3 are responsible for β-arrestin activation, leading to receptor internalization. Our results suggest that distinct D1R GRK phosphorylation sites are involved in β-arrestin binding and activation.
Keywords: D1 receptor; dopamine; phosphorylation; β-arrestin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 Selectively Enhances β-Arrestin Recruitment to the D2 Dopamine Receptor through Mechanisms That Are Independent of Receptor Phosphorylation.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 20;13(10):1552. doi: 10.3390/biom13101552. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892234 Free PMC article.
-
The role of G protein-coupled receptor kinases in GLP-1R β-arrestin recruitment and internalisation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Apr;222:116119. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116119. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38461904
-
Role of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase site serine cluster in beta2-adrenergic receptor internalization, desensitization, and beta-arrestin translocation.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 17;281(11):7684-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500328200. Epub 2006 Jan 3. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16407241
-
Double life: How GRK2 and β-arrestin signaling participate in diseases.Cell Signal. 2022 Jun;94:110333. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110333. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Cell Signal. 2022. PMID: 35430346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation barcoding as a mechanism of directing GPCR signaling.Sci Signal. 2011 Aug 9;4(185):pe36. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002331. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 21868354 Review.
Cited by
-
G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 Selectively Enhances β-Arrestin Recruitment to the D2 Dopamine Receptor through Mechanisms That Are Independent of Receptor Phosphorylation.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 20;13(10):1552. doi: 10.3390/biom13101552. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892234 Free PMC article.
-
Arrestin-3-assisted activation of JNK3 mediates dopaminergic behavioral sensitization.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Jul 16;5(7):101623. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101623. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 38936368 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

