Pathophysiological Involvement of Mast Cells and the Lipid Mediators in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling
- PMID: 37047587
- PMCID: PMC10094825
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076619
Pathophysiological Involvement of Mast Cells and the Lipid Mediators in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling
Abstract
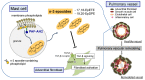
Mast cells are responsible for IgE-dependent allergic responses, but they also produce various bioactive mediators and contribute to the pathogenesis of various cardiovascular diseases, including pulmonary hypertension (PH). The importance of lipid mediators in the pathogenesis of PH has become evident in recent years, as exemplified by prostaglandin I2, the most central therapeutic target in pulmonary arterial hypertension. New bioactive lipids other than eicosanoids have also been identified that are associated with the pathogenesis of PH. However, it remains largely unknown how mast cell-derived lipid mediators are involved in pulmonary vascular remodeling. Recently, it has been demonstrated that mast cells produce epoxidized n-3 fatty acid (n-3 epoxides) in a degranulation-independent manner, and that n-3 epoxides produced by mast cells regulate the abnormal activation of pulmonary fibroblasts and suppress the progression of pulmonary vascular remodeling. This review summarizes the role of mast cells and bioactive lipids in the pathogenesis of PH. In addition, we introduce the pathophysiological role and therapeutic potential of n-3 epoxides, a mast cell-derived novel lipid mediator, in the pulmonary vascular remodeling in PH. Further knowledge of mast cells and lipid mediators is expected to lead to the development of innovative therapies targeting pulmonary vascular remodeling.
Keywords: lipid mediator; mast cell; n-3 epoxides; omega-3; pulmonary hypertension; remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p38 MAPK signaling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease pathogenesis and inhibitor therapeutics.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Nov 2;21(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01337-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37919729 Free PMC article.
-
The nitrofen/bisdiamine murine model of congenital diaphragmatic hernia has a pulmonary hypertension vascular phenotype consistent with human CDH.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2025 Jul 1;329(1):L48-L60. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00233.2024. Epub 2025 May 30. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40445713 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Topical antihistamines and mast cell stabilisers for treating seasonal and perennial allergic conjunctivitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 1;2015(6):CD009566. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009566.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26028608 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advances and applications of biosensors in pulmonary hypertension.Respir Res. 2025 Apr 15;26(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03221-w. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 40234824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CC chemokines Modulate Immune responses in Pulmonary Hypertension.J Adv Res. 2024 Sep;63:171-186. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.10.015. Epub 2023 Nov 4. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37926143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive analysis of genes associated with hypoxia and cuproptosis in pulmonary arterial hypertension using machine learning methods and immune infiltration analysis: AHR is a key gene in the cuproptosis process.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 26;11:1435068. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1435068. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39391037 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Remodeling: The Multicellular Mechanisms of Pulmonary Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 30;26(9):4265. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094265. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: From the Pathogenesis to Clinical Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;25(15):8427. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158427. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wagenvoort C.A. The pathology of primary pulmonary hypertension. J. Pathol. 1970;101:51A–54A. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

