Towards a More Realistic In Vitro Meat: The Cross Talk between Adipose and Muscle Cells
- PMID: 37047600
- PMCID: PMC10095036
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076630
Towards a More Realistic In Vitro Meat: The Cross Talk between Adipose and Muscle Cells
Abstract
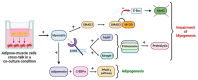
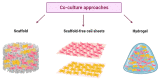
According to statistics and future predictions, meat consumption will increase in the coming years. Considering both the environmental impact of intensive livestock farming and the importance of protecting animal welfare, the necessity of finding alternative strategies to satisfy the growing meat demand is compelling. Biotechnologies are responding to this demand by developing new strategies for producing meat in vitro. The manufacturing of cultured meat has faced criticism concerning, above all, the practical issues of culturing together different cell types typical of meat that are partly responsible for meat's organoleptic characteristics. Indeed, the existence of a cross talk between adipose and muscle cells has critical effects on the outcome of the co-culture, leading to a general inhibition of myogenesis in favor of adipogenic differentiation. This review aims to clarify the main mechanisms and the key molecules involved in this cross talk and provide an overview of the most recent and successful meat culture 3D strategies for overcoming this challenge, focusing on the approaches based on farm-animal-derived cells.
Keywords: cells co-culture; farm-animal-derived cells; hydrogel; in vitro meat; muscle and adipose cell cross talk; scaffold.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mimicking Wagyu beef fat in cultured meat: Progress in edible bovine adipose tissue production with controllable fatty acid composition.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Jun 30;21:100720. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100720. eCollection 2023 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 37455817 Free PMC article.
-
Review: Will "cultured meat" transform our food system towards more sustainability?Animal. 2025 Feb;19 Suppl 1:101145. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2024.101145. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Animal. 2025. PMID: 38670917 Review.
-
The Myth of Cultured Meat: A Review.Front Nutr. 2020 Feb 7;7:7. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2020.00007. eCollection 2020. Front Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32118026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cultured meat from stem cells: challenges and prospects.Meat Sci. 2012 Nov;92(3):297-301. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.04.008. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Meat Sci. 2012. PMID: 22543115 Review.
-
Isolation and Characterization of Tissue Resident CD29-Positive Progenitor Cells in Livestock to Generate a Three-Dimensional Meat Bud.Cells. 2021 Sep 21;10(9):2499. doi: 10.3390/cells10092499. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572147 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into muscle cells to constitute cultured meat with tunable intramuscular fat deposition.Elife. 2024 May 21;13:RP93220. doi: 10.7554/eLife.93220. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38771186 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of CO2-Triggered Extrudable Chitosan for Fat Production.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025 Aug 11;11(8):4714-4724. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5c01005. Epub 2025 Jul 16. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025. PMID: 40667853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benton T., Bieg C., Harwatt H., Pudassaini R., Wellesley L. Food System Impacts on Biodiversity Loss Three Levers for Food. Chatham House; London, UK: 2021.
-
- FAO . FAO Publications Catalogue 2022. FAO; Rome, Italy: 2023. - DOI
-
- International Energy Agency Global Energy Review: CO2 Emissions in 2021. Global Emissions Rebound Sharply to Highest Ever Level. 2021. [(accessed on 13 March 2023)]. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-co2-emissions-in-2021-2.

