Blood-Brain Barrier Biomarkers before and after Kidney Transplantation
- PMID: 37047601
- PMCID: PMC10095132
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076628
Blood-Brain Barrier Biomarkers before and after Kidney Transplantation
Abstract
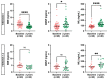
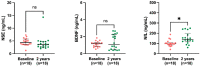
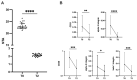
Kidney transplantation (KT) may improve the neurological status of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients, reflected by the altered levels of circulating BBB-specific biomarkers. This study compares the levels of neuron specific enolase (NSE), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurofilament light chain (NfL), and circulating plasma extracellular vesicles (EVs) in kidney-failure patients before KT and at a two-year follow up. Using ELISA, NSE, BDNF, and NfL levels were measured in the plasma of 74 living-donor KT patients. Plasma EVs were isolated with ultracentrifugation, and characterized for concentration/size and surface protein expression using flow cytometry from a subset of 25 patients. Lower NSE levels, and higher BDNF and NfL were observed at the two-year follow-up compared to the baseline (p < 0.05). Male patients had significantly higher BDNF levels compared to those of females. BBB biomarkers correlated with the baseline lipid profile and with glucose, vitamin D, and inflammation markers after KT. BBB surrogate marker changes in the microcirculation of early vascular aging phenotype patients with calcification and/or fibrosis were observed only in NSE and BDNF. CD31+ microparticles from endothelial cells expressing inflammatory markers such as CD40 and integrins were significantly reduced after KT. KT may, thus, improve the neurological status of CKD patients, as reflected by changes in BBB-specific biomarkers.
Keywords: BBB; BDNF; CKD; NSE; NfL; end-stage kidney failure; extracellular vesicles; kidney transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Blood-brain barrier and gut barrier dysfunction in chronic kidney disease with a focus on circulating biomarkers and tight junction proteins.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 15;12(1):4414. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08387-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35292710 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and oxidation: do they improve after kidney transplantation? Relationship with mortality after transplantation.Int Urol Nephrol. 2017 Mar;49(3):533-540. doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1435-4. Epub 2016 Dec 24. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28013471
-
Cerebral Biomarkers and Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity in Preeclampsia.Cells. 2022 Feb 24;11(5):789. doi: 10.3390/cells11050789. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269411 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological Characteristics of Periodontal Disease in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Kidney Transplantation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 11;20(14):3413. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143413. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31336777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): a multifaceted marker in chronic kidney disease.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2022 Dec;26(12):1149-1159. doi: 10.1007/s10157-022-02268-z. Epub 2022 Aug 28. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 36030459 Review.
Cited by
-
Choroid plexus enlargement in patients with end-stage renal disease: implications for glymphatic system dysfunction.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 14;15:1459356. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1459356. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39469069 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in chronic kidney disease: integrated clinical and experimental evidence.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Jul 28;12:1627534. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1627534. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40791659 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of intraoperative fluid for kidney transplantation.Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2025 Jan;20(1):14-22. doi: 10.17085/apm.24180. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2025. PMID: 39923768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability and Cognitive Impairment in Patients With ESKD.Kidney Int Rep. 2024 Jul 20;9(10):2988-2995. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.07.021. eCollection 2024 Oct. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 39430169 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial polarization pathways and therapeutic drugs targeting activated microglia in traumatic brain injury.Neural Regen Res. 2026 Jan 1;21(1):39-56. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00810. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Neural Regen Res. 2026. PMID: 39665832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bikbov B., Purcell C.A., Levey A.S., Smith M., Abdoli A., Abebe M., Adebayo O.M., Afarideh M., Agarwal S.K., Agudelo-Botero M., et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2020;395:709–733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murton M., Goff-Leggett D., Bobrowska A., Garcia Sanchez J.J., James G., Wittbrodt E., Nolan S., Sörstadius E., Pecoits-Filho R., Tuttle K. Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease by KDIGO Categories of Glomerular Filtration Rate and Albuminuria: A Systematic Review. Adv. Ther. 2021;38:180–200. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01568-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xie Y., Bowe B., Mokdad A.H., Xian H., Yan Y., Li T., Maddukuri G., Tsai C.-Y., Floyd T., Al-Aly Z. Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study Highlights the Global, Regional, and National Trends of Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology from 1990 to 2016. Kidney Int. 2018;94:567–581. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.04.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stenvinkel P., Larsson T.E. Chronic Kidney Disease: A Clinical Model of Premature Aging. Volume 62. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2013. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Vetenskapsrådet 2018-00932 GOING-FWD/CIMED, Heart and Lung Foundation, Westman and Swedish Medical Research Council; GENDER-NET Plus ERA-NET Initiative
- "Departments of Excel-lence 2018-2022", AGING Project-Department of Translational Medicine (DIMET), University of Piemonte Orientale (UPO/Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR) program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

