Δ8-THC Protects against Amyloid Beta Toxicity Modulating ER Stress In Vitro: A Transcriptomic Analysis
- PMID: 37047608
- PMCID: PMC10095455
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076598
Δ8-THC Protects against Amyloid Beta Toxicity Modulating ER Stress In Vitro: A Transcriptomic Analysis
Abstract
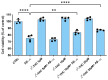
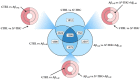
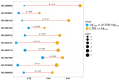
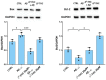
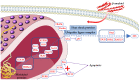
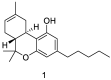
Alzheimer's disease (AD) represents the most common form of dementia, characterized by amyloid β (Aβ) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). It is characterized by neuroinflammation, the accumulation of misfolded protein, ER stress and neuronal apoptosis. It is of main importance to find new therapeutic strategies because AD prevalence is increasing worldwide. Cannabinoids are arising as promising neuroprotective phytocompounds. In this study, we evaluated the neuroprotective potential of Δ8-THC pretreatment in an in vitro model of AD through transcriptomic analysis. We found that Δ8-THC pretreatment restored the loss of cell viability in retinoic acid-differentiated neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells treated with Aβ1-42. Moreover, the transcriptomic analysis provided evidence that the enriched biological processes of gene ontology were related to ER functions and proteostasis. In particular, Aβ1-42 upregulated genes involved in ER stress and unfolded protein response, leading to apoptosis as demonstrated by the increase in Bax and the decrease in Bcl-2 both at gene and protein expression levels. Moreover, genes involved in protein folding and degradation were also deregulated. On the contrary, Δ8-THC pretreatment reduced ER stress and, as a consequence, neuronal apoptosis. Then, the results demonstrated that Δ8-THC might represent a new neuroprotective agent in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; neuronal apoptosis; unfolded protein response; Δ8-THC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Durairajan S.S.K., Selvarasu K., Bera M.R., Rajaram K., Iyaswamy A., Li M. Alzheimer’s Disease and other Tauopathies: Exploring Efficacy of Medicinal Plant-derived Compounds in Alleviating Tau-mediated Neurodegeneration. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2022;15:361–379. doi: 10.2174/1874467214666210906125318. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kumar A., Sidhu J., Goyal A., Tsao J.W. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. Alzheimer Disease.
-
- Petit D., Fernandez S.G., Zoltowska K.M., Enzlein T., Ryan N.S., O’Connor A., Szaruga M., Hill E., Vandenberghe R., Fox N.C., et al. Aβ profiles generated by Alzheimer’s disease causing PSEN1 variants determine the pathogenicity of the mutation and predict age at disease onset. Mol. Psychiatry. 2022;27:2821–2832. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01518-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

