The Efficacy of Tumor Mutation Burden as a Biomarker of Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
- PMID: 37047684
- PMCID: PMC10095310
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076710
The Efficacy of Tumor Mutation Burden as a Biomarker of Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Abstract
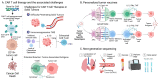
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death in the world; therefore, extensive research has been dedicated to exploring potential therapeutics, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Initially, programmed-death ligand-1 was the biomarker utilized to predict the efficacy of ICIs. However, its heterogeneous expression in the tumor microenvironment, which is critical to cancer progression, promoted the exploration of the tumor mutation burden (TMB). Research in various cancers, such as melanoma and lung cancer, has shown an association between high TMB and response to ICIs, increasing its predictive value. However, the TMB has failed to predict ICI response in numerous other cancers. Therefore, future research is needed to analyze the variations between cancer types and establish TMB cutoffs in order to create a more standardized methodology for using the TMB clinically. In this review, we aim to explore current research on the efficacy of the TMB as a biomarker, discuss current approaches to overcoming immunoresistance to ICIs, and highlight new trends in the field such as liquid biopsies, next generation sequencing, chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, and personalized tumor vaccines.
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; tumor microenvironment; tumor mutation burden.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Li M.M., Datto M., Duncavage E.J., Kulkarni S., Lindeman N.I., Roy S., Tsimberidou A.M., Vnencak-Jones C.L., Wolff D.J., Younes A., et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation and Reporting of Sequence Variants in Cancer: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and College of American Pathologists. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017;19:4–23. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2016.10.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng D.T., Mitchell T.N., Zehir A., Shah R.H., Benayed R., Syed A., Chandramohan R., Liu Z.Y., Won H.H., Scott S.N., et al. Memorial Sloan Kettering-Integrated Mutation Profiling of Actionable Cancer Targets (MSK-IMPACT): A Hybridization Capture-Based Next-Generation Sequencing Clinical Assay for Solid Tumor Molecular Oncology. J. Mol. Diagn. 2015;17:251–264. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2014.12.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

