Investigation of Dynamic Behavior of Confined Ionic Liquid [BMIM]+[TCM]- in Silica Material SBA-15 Using NMR
- PMID: 37047711
- PMCID: PMC10095388
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076739
Investigation of Dynamic Behavior of Confined Ionic Liquid [BMIM]+[TCM]- in Silica Material SBA-15 Using NMR
Abstract
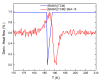
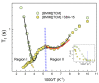
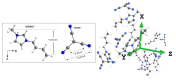
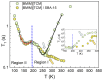
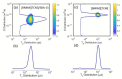
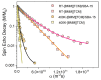
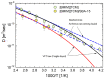
The molecular dynamics of 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium tricyanomethanide ionic liquid [BMIM]+[TCM]- confined in SBA-15 mesoporous silica were examined using 1H NMR spin-lattice (T1) relaxation and diffusion measurements. An extensive temperature range (100 K-400 K) was considered in order to study both the liquid and glassy states. The hydrogen dynamics in the two states and the self-diffusion coefficients of the cation [BMIM]+ above the glass transition temperature were extracted from the experimental data. The results were then compared to the corresponding bulk substance. The effects of confinement on the dynamic properties of the ionic liquid clearly manifest themselves in both temperature regimes. In the high-temperature liquid state, the mobility of the confined cations reduces significantly compared to the bulk; interestingly, confinement drives the ionic liquid to the glassy state at a higher temperature Tg than the bulk ionic liquid, whereas an unusual T1 temperature dependence is observed in the high-temperature regime, assigned to the interaction of the ionic liquid with the silica-OH species.
Keywords: NMR; confined ionic liquids; mesoporous silica SBA-15; relaxation and diffusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic and structural properties of room-temperature ionic liquids near silica and carbon surfaces.Langmuir. 2013 Aug 6;29(31):9744-9. doi: 10.1021/la401172z. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Langmuir. 2013. PMID: 23845079
-
Determining diffusion coefficients of ionic liquids by means of field cycling nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry.J Chem Phys. 2014 Jun 28;140(24):244509. doi: 10.1063/1.4882064. J Chem Phys. 2014. PMID: 24985656
-
Nuclear magnetic relaxation and diffusion study of the ionic liquids 1-ethyl- and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide confined in porous glass.Magn Reson Chem. 2019 Aug;57(10):818-828. doi: 10.1002/mrc.4852. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Magn Reson Chem. 2019. PMID: 30770585
-
Multiscale nuclear magnetic relaxation dispersion of complex liquids in bulk and confinement.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2018 Feb;104:12-55. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2017.11.001. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2018. PMID: 29405980 Review.
-
Small Molecules, Non-Covalent Interactions, and Confinement.Molecules. 2020 Jul 21;25(14):3311. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143311. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32708283 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- He F., Wang L.-M., Richert R. Confined Viscous Liquids: Interfacial versus Finite Size Effects. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2007;141:3–9. doi: 10.1140/epjst/e2007-00008-0. - DOI
-
- Gupta A.K., Verma Y.L., Singh R.K., Chandra S. Studies on an Ionic Liquid Confined in Silica Nanopores: Change in T g and Evidence of Organic–Inorganic Linkage at the Pore Wall Surface. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2014;118:1530–1539. doi: 10.1021/jp408142a. - DOI
-
- Broussely M., Biensan P., Bonhomme F., Blanchard P., Herreyre S., Nechev K., Staniewicz R.J. Main Aging Mechanisms in Li Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources. 2005;146:90–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.03.172. - DOI
-
- Balducci A., Yin Z., Zhang X., Tu Z., Hu X., Wu Y. Ionic Liquids for Hybrid Supercapacitors. Electrochem. Commun. 2004;6:566–570. doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2004.04.005. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

