Unveiling the Differences in Signaling and Regulatory Mechanisms between Dopamine D2 and D3 Receptors and Their Impact on Behavioral Sensitization
- PMID: 37047716
- PMCID: PMC10095578
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076742
Unveiling the Differences in Signaling and Regulatory Mechanisms between Dopamine D2 and D3 Receptors and Their Impact on Behavioral Sensitization
Abstract
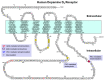
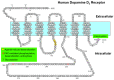
Dopamine receptors are classified into five subtypes, with D2R and D3R playing a crucial role in regulating mood, motivation, reward, and movement. Whereas D2R are distributed widely across the brain, including regions responsible for motor functions, D3R are primarily found in specific areas related to cognitive and emotional functions, such as the nucleus accumbens, limbic system, and prefrontal cortex. Despite their high sequence homology and similar signaling pathways, D2R and D3R have distinct regulatory properties involving desensitization, endocytosis, posttranslational modification, and interactions with other cellular components. In vivo, D3R is closely associated with behavioral sensitization, which leads to increased dopaminergic responses. Behavioral sensitization is believed to result from D3R desensitization, which removes the inhibitory effect of D3R on related behaviors. Whereas D2R maintains continuous signal transduction through agonist-induced receptor phosphorylation, arrestin recruitment, and endocytosis, which recycle and resensitize desensitized receptors, D3R rarely undergoes agonist-induced endocytosis and instead is desensitized after repeated agonist exposure. In addition, D3R undergoes more extensive posttranslational modifications, such as glycosylation and palmitoylation, which are needed for its desensitization. Overall, a series of biochemical settings more closely related to D3R could be linked to D3R-mediated behavioral sensitization.
Keywords: biased signaling; desensitization; dimerization; dopamine D2 and D3 receptor; intracellular trafficking; posttranslational modification; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RalA employs GRK2 and β-arrestins for the filamin A-mediated regulation of trafficking and signaling of dopamine D2 and D3 receptor.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Aug;1863(8):2072-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.05.010. Epub 2016 May 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27188791
-
Presynaptic and Postsynaptic Mesolimbic Dopamine D3 Receptors Play Distinct Roles in Cocaine Versus Opioid Reward in Mice.Biol Psychiatry. 2024 Nov 1;96(9):752-765. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2024.05.020. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Biol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38838841
-
Biased signaling agonist of dopamine D3 receptor induces receptor internalization independent of β-arrestin recruitment.Pharmacol Res. 2019 May;143:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30844536
-
Current drug treatments targeting dopamine D3 receptor.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Sep;165:164-77. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.06.007. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27343365 Review.
-
Targeting the dopamine D3 receptor: an overview of drug design strategies.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016 Jul;11(7):641-64. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2016.1185413. Epub 2016 May 30. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27135354 Review.
Cited by
-
PKC in the perspective of dopamine receptor signaling.Acta Biochim Pol. 2025 Jun 9;72:14488. doi: 10.3389/abp.2025.14488. eCollection 2025. Acta Biochim Pol. 2025. PMID: 40552006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of positive mGlu5 modulation on D2 signaling and nicotine-conditioned place preference: Mechanisms of epigenetic inheritance in a transgenerational model of drug abuse vulnerability in psychosis.J Psychopharmacol. 2025 Mar;39(3):265-281. doi: 10.1177/02698811241292902. Epub 2024 Oct 27. J Psychopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39462877 Free PMC article.
-
Arrestin-3-assisted activation of JNK3 mediates dopaminergic behavioral sensitization.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Jul 16;5(7):101623. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101623. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 38936368 Free PMC article.
-
CHL1 depletion affects dopamine receptor D2-dependent modulation of mouse behavior.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Nov 9;17:1288509. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1288509. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38025382 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Neuron and Astrocyte Dopamine Receptors via Receptor-Receptor Interactions.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 8;16(10):1427. doi: 10.3390/ph16101427. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895898 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

