Dysregulation of Resolvin E1 Metabolism and Signaling in a Light-Damage Model of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- PMID: 37047721
- PMCID: PMC10095591
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076749
Dysregulation of Resolvin E1 Metabolism and Signaling in a Light-Damage Model of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Abstract
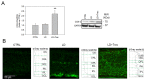
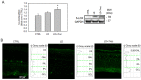
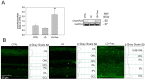
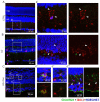
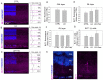
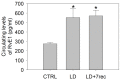
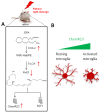
Resolvin E1 (RvE1) is an eicosapentaenoic acid-derived lipid mediator involved in the resolution of inflammation. Here, we investigated whether RvE1 alterations may occur in an animal model of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). To this end, Sprague Dawley albino rats underwent light damage (LD), and retinas and serum were analyzed immediately or seven days after treatment. Western blot of retinas showed that the RvE1 receptor ChemR23 and the RvE1 metabolic enzymes 5-LOX and COX-2 were unchanged immediately after LD, but they were significantly up-regulated seven days later. Instead, the RvE1 receptor BLT1 was not modulated by LD, and neither was the RvE1 degradative enzyme 15-PGDH. Moreover, ChemR23, 5-LOX, COX-2 and BLT1 were found to be more expressed in the inner retina under all experimental conditions, as observed through ImageJ plot profile analysis. Of note, amacrine cells highly expressed BLT1, while ChemR23 was highly expressed in the activated microglia of the outer retina. ELISA assays also showed that LD rats displayed significantly higher circulating levels and reduced retinal levels of RvE1 compared to controls. Altogether, our data indicate that RvE1 metabolism and signaling are modulated in the LD model, suggesting a potentially relevant role of this pathway in AMD.
Keywords: RvE1; SPMs; age-related macular degeneration; bioactive lipids; light damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Serhan C.N., Hong S., Gronert K., Colgan S.P., Devchand P.R., Mirick G., Moussignac R.L. Resolvins: A family of bioactive products of omega-3 fatty acid transformation circuits initiated by aspirin treatment that counter proinflammation signals. J. Exp. Med. 2002;196:1025–1037. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020760. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rossi S., Di Filippo C., Gesualdo C., Potenza N., Russo A., Trotta M.C., Zippo M.V., Maisto R., Ferraraccio F., Simonelli F., et al. Protection from endotoxic uveitis by intravitreal resolvin D1: Involvement of lymphocytes, miRNAs, ubiquitin-proteasome, and M1/M2 macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015;2015:149381. doi: 10.1155/2015/149381. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

