Determination of Phenol with Peroxidase Immobilized on CaCO3
- PMID: 37047739
- PMCID: PMC10094929
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076766
Determination of Phenol with Peroxidase Immobilized on CaCO3
Abstract
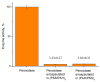
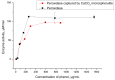
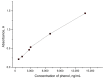
Phenols are widely used in industries despite their toxicity, which requires governments to limit their concentration in water to 5 mg/L before discharge to the city sewer. Thus, it is essential to develop a rapid, simple, and low-cost detection method for phenol. This study explored two pathways of peroxidase immobilization to develop a phenol detection system: peroxidase encapsulation into polyelectrolyte microcapsules and peroxidase captured by CaCO3. The encapsulation of peroxidase decreased enzyme activity by 96%; thus, this method cannot be used for detection systems. The capturing process of peroxidase by CaCO3 microspherulites did not affect the maximum reaction rate and the Michaelis constant of peroxidase. The native peroxidase-Vmax = 109 µM/min, Km = 994 µM; CaCO3-peroxidase-Vmax = 93.5 µM/min, Km = 956 µM. Ultimately, a reusable phenol detection system based on CaCO3 microparticles with immobilized peroxidase was developed, capable of detecting phenol in the range of 700 ng/mL to 14 µg/mL, with an error not exceeding 5%, and having a relatively low cost and production time. The efficiency of the system was confirmed by determining the content of phenol in a paintwork product.
Keywords: CaCO3 particles; enzyme detection system; peroxidase; phenol; phenol detection system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phenols removal by immobilized horseradish peroxidase.J Hazard Mater. 2009 Jul 30;166(2-3):1082-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.026. Epub 2008 Dec 7. J Hazard Mater. 2009. PMID: 19144465
-
Enzymatic removal of phenol and p-chlorophenol in enzyme reactor: horseradish peroxidase immobilized on magnetic beads.J Hazard Mater. 2008 Aug 15;156(1-3):148-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.12.008. Epub 2007 Dec 8. J Hazard Mater. 2008. PMID: 18207637
-
Characterization and application of biochar-immobilized crude horseradish peroxidase for removal of phenol from water.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021 Dec;208:112038. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.112038. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021. PMID: 34454363
-
Treatment of phenolic wastewater by horseradish peroxidase immobilized by bioaffinity layering.Chemosphere. 2007 Mar;67(4):741-7. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.10.043. Epub 2006 Nov 30. Chemosphere. 2007. PMID: 17140630
-
Recent development in the application of immobilized oxidative enzymes for bioremediation of hazardous micropollutants - A review.Chemosphere. 2020 Jan;239:124716. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124716. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Chemosphere. 2020. PMID: 31521938 Review.
References
-
- Khatri N., Tyagi S. Influences of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors on Surface and Groundwater Quality in Rural and Urban Areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015;8:23–39. doi: 10.1080/21553769.2014.933716. - DOI
-
- Manasa R.L., Mehta A. Wastewater: Sources of Pollutants and Its Remediation. In: Lichtfouse E., Schwarzbauer J., Robert D., editors. Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2020. pp. 197–219.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

