Salus Platform: A Digital Health Solution Tool for Managing Syphilis Cases in Brazil-A Comparative Analysis
- PMID: 37047873
- PMCID: PMC10094047
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20075258
Salus Platform: A Digital Health Solution Tool for Managing Syphilis Cases in Brazil-A Comparative Analysis
Abstract
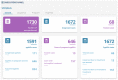
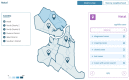
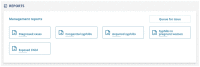
(1) Introduction: Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that constitutes a serious public health problem in Brazil and worldwide; (2) Methods: This was a descriptive and exploratory study that sought to analyze and compare the characteristics of Brazilian health systems with a new platform (Salus) developed by the Laboratory of Technological Innovation in Health in the scope of notification and management of disease data, including syphilis. In addition, this analysis aimed to assess whether Salus fully meets the necessary data management fields and can be indicated as a tool to improve health management in the context of syphilis in Brazil. (3) Results: In this study, the Salus functionalities were demonstrated and compared with the current Brazilian systems by discovering the existing gaps in the evaluated systems. The gaps found may explain the delay in meeting demands, the difficulty of making routine therapeutic follow-ups, in addition to interference with the vital purpose of follow-up in the epidemiological surveillance of diseases. As a result, Salus demonstrates functionalities that surpass all others and meet case management demands in a superior way to the systems currently used in the country. (4) Conclusions: The Brazilian health information systems related to the response to syphilis do not fulfill the purpose for which they were developed. Instead, they contribute to the fragmentation of health data and information, delays in diagnosis, incomplete case management, and loss of data due to inconsistencies and inadequate reporting. In addition, they are systems without interconnection, which do not articulate epidemiological surveillance actions with primary health care. All these factors may be obscuring accurate data on syphilis in Brazil, resulting in high and unnecessary public spending and late care for users of the Unified Health System (SUS).
Keywords: Salus; acquired syphilis; congenital syphilis; epidemiological monitoring; information system; maternal syphilis; primary attention; sexual infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be interpreted as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Secretariat of Health Surveillance, Ministry of Health Syphilis 2020. Special Epidemiological Bulletin 2020; Department of Diseases of Chronic Conditions and Sexually Transmitted Infections. [(accessed on 3 June 2022)]; Available online: https://www.gov.br/aids/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/boletins-epidemiologi....
-
- De Brito Pinto T.K., da Cunha-Oliveira A.C.G.D.P., Sales-Moioli A.I.L., Dantas J.F., da Costa R.M.M., Silva Moura J.P., Gómez-Cantarino S., Valentim R.A.M. Clinical Protocols and Treatment Guidelines for the Management of Maternal and Congenital Syphilis in Brazil and Portugal: Analysis and Comparisons: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022;19:10513. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191710513. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kleber G., Alves D., de Paiva J., Diógenes D., Valentim R., Medeiros A. SOS Syphilis: Smartphone application for the mapping of syphilis attention networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021;181:434–441. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2021.01.188. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

