Analysis of Publication Activity and Research Trends in the Field of AI Medical Applications: Network Approach
- PMID: 37047950
- PMCID: PMC10094658
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20075335
Analysis of Publication Activity and Research Trends in the Field of AI Medical Applications: Network Approach
Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized numerous industries, including medicine. In recent years, the integration of AI into medical practices has shown great promise in enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and personalizing treatment plans. This paper aims at the exploration of the AI-based medicine research using network approach and analysis of existing trends based on PubMed. Our findings are based on the results of PubMed search queries and analysis of the number of papers obtained by the different search queries. Our goal is to explore how are the AI-based methods used in healthcare research, which approaches and techniques are the most popular, and to discuss the potential reasoning behind the obtained results. Using analysis of the co-occurrence network constructed using VOSviewer software, we detected the main clusters of interest in AI-based healthcare research. Then, we proceeded with the thorough analysis of publication activity in various categories of medical AI research, including research on different AI-based methods applied to different types of medical data. We analyzed the results of query processing in the PubMed database over the past 5 years obtained via a specifically designed strategy for generating search queries based on the thorough selection of keywords from different categories of interest. We provide a comprehensive analysis of existing applications of AI-based methods to medical data of different modalities, including the context of various medical fields and specific diseases that carry the greatest danger to the human population.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; artificial neural network; deep learning; machine learning; medical area; medical data; supervised learning; unsupervised learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders and organizations had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
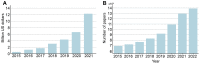

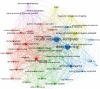



References
-
- Topol E. Deep Medicine: How Artificial Intelligence Can Make Healthcare Human Again. Hachette; London, UK: 2019.
-
- Zhang C., Lu Y. Study on artificial intelligence: The state of the art and future prospects. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2021;23:100224. doi: 10.1016/j.jii.2021.100224. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

